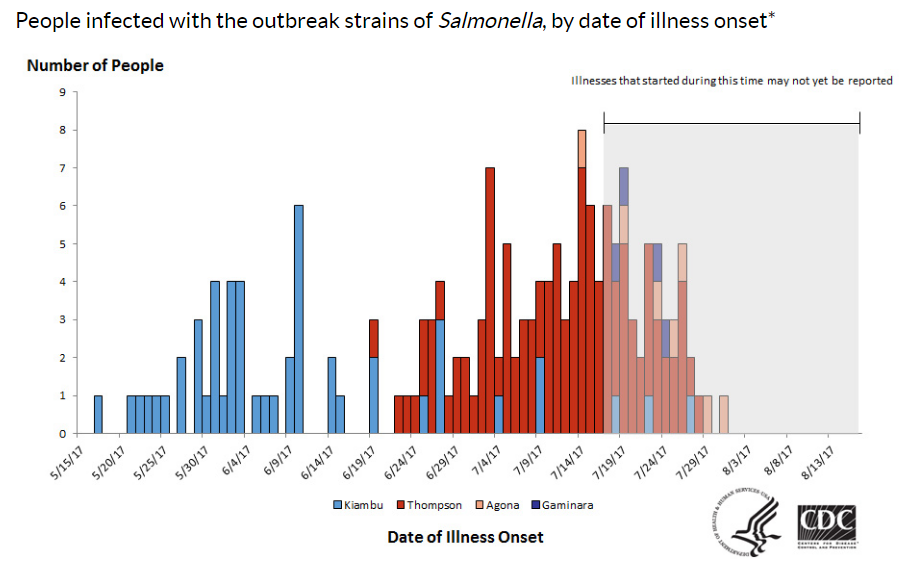
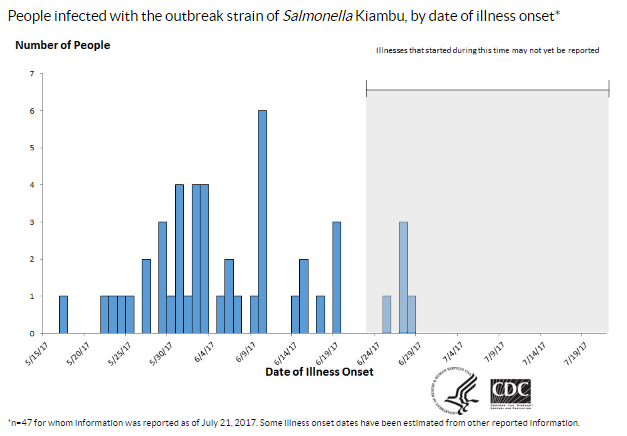
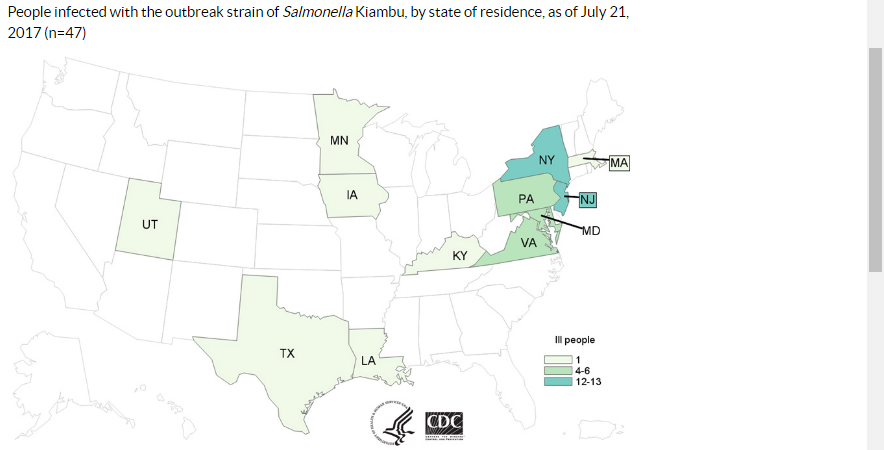
Ellen K. Silbergeld. : How Industrial Meat Production Endangers Workers, Animals, and Consumers. Johns Hopkins Press, 2016.

Ellen Silbergeld, a professor of environmental health sciences, epidemiology, and health policy at Hopkins, has long been a strong advocate for getting toxic substances out of our food supply. Here, she takes on our system of industrial farm animal production in a plea for better treatment of everyone and everything involved in it.
Big issue #1: the use of antibiotics as growth promoters. This not only induces bacteria to become resistant to those drugs, but also is unnecessary.
Big issue #2: the failure of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point—the method for preventing food safety problems) to prevent harmful, antibiotic-resistant bacteria from reaching the public.
Overall, she says:
The inextricable relationship between industrial food animal production and the environment challenges us in two ways. First, we are all at risk–not just those of us who consume the products of industrially raised animals–and second, decontaminating food products will not contain the public health problems of this industry. It is time to think about industrial food animal production as an industry in terms of environmental pollution, and it is long overdue to recognize that its pollution footprint, like its production, is industrial in scale (p. 127).
As for the remedy, “agriculture is an industry, and as such it carries certain obligations.” These include, among others:
- Industries must abide by laws that prevent monopolization, price fixing, and overconcentration.
- Industries must bear full liability for unsafe products.
- Industries must obey the labor laws of the country.
She has plenty more to say about government’s role in all this.
Our role is to insist that industry and government follow and apply laws. We had best get busy.