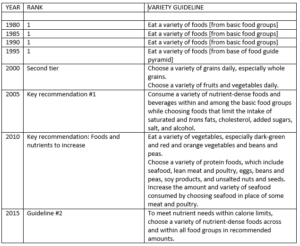
Coca-Cola wants the 2020 dietary guidelines to say more about beverages
I am indebted to Margarita Raycheva, who writes for the highly informative newsletter, IEG Policy Agribusiness, for her recent article, which certainly got my attention: “Coca-Cola asks DGAC to develop detailed dietary recommendations for beverages” (this is probably behind a paywall).
Her article is about comments filed by Coca-Cola to the DGAC, the 2020 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee. She did not provide a link to those comments, so I had to search for them. This involved finding the DGAC comments page, searching for Coca-Cola, locating the company’s letter, and opening the pdf attachment.
The 12-page document reads like a highly sophisticated advertisement for Coca-Cola’s astounding number of beverage options, many of them low in sugar or sugar-free.
Over the last few years, Coca-Cola has been transforming to become a total beverage company that meets Americans’ fast-changing preferences across a wide array of beverage categories. We support the World Health Organization’s recommendation that people should limit added sugar to no more than 10% of their total daily calorie consumption1 and are rethinking existing recipes, package sizes and offerings to ensure we are helping consumers manage their daily intake of added sugar and other nutrients from our portfolio. Today, we offer more than 800 drinks in the U.S. alone, ranging from soft drinks to juices, teas, coffee, dairy, sports drinks, water and more – more than 250 of which are low- or zero-sugar options. More than 40% of our sparkling beverage brands in the U.S. are now available in package sizes that are smaller than 8.5 ounces. We are increasing marketing support for low-sugar, no-sugar and unsweetened products…; we are introducing less sweet versions of classic soft drinks…; and we are accelerating our expansion into new beverage categories through the acquisition of brands….We are taking these actions because we recognize the critical role that we – and the entire industry – can play in advancing nutritional goals by using our scale for good.
Why do this?
• About 15% of energy comes from beverages
• Beverages, such as sweetened soft drinks, coffee and tea contribute more than 40% of daily added sugar intake
• Beverages, mainly milk and 100% juice, contribute over 40% of vitamin C and D intake and more than 20% intake of carbohydrates, calcium, potassium and magnesium
• Fruit intake (0.9 cup/day) is half of recommended levels (2 cups/day); 100% fruit juice contributes up to 24% of fruit intake in children, but decreases after adolescence
• Coffee and tea contribute up to 12% of potassium intake in adults
• Waters contribute up to 10% of calcium intake in adults
In other words, drink more (of our) beverages!
Coca-Cola’s proposals for how beverages can enhance diets:
- Hydration
- Nutrition and health
- Enjoyment
- Performance
What should the DGAC do?
By creating a framework that includes guidance for all types of beverages, the DGA can help drive Americans towards healthier versions of drinks they are typically consuming. Recommending limited
consumption or small shifts towards healthier beverages is more effective than simply discouraging the consumption of entire beverage categories.
The company’s proposals for how the DGAC can help it sell more beverages include sample statements like these examples [with my translations]:
- Water should be the primary beverage choice [recommend our bottled water]
- Milk plays an important role in development and health, and contributes essential nutrients to healthy eating patterns, including protein, calcium, vitamin D and potassium [recommend our milk drinks]
- When fortified, plant-based beverages may provide nutrients and support consumer choice, but generally should not be considered a replacement for dairy [please don’t recommend almond, soy, or oat milks–we don’t make any of those drinks]
- Juice contributes to the public’s consumption of essential nutrients, phytonutrient and fruit/vegetable intake [recommend our juice drinks]
- Coffee and tea are sources of health-promoting phytonutrients and are associated with reduced risk of rtain non-communicable diseases (NCDs) [recommend them; we sell those too]
- Replace sugar-sweetened beverages >40 kcal that do not contribute significantly to nutrition needs with these beverages to reduce calorie and sugar consumption [if you must recommend avoing sugary beverages, at least recommend replacement with everything else we sell]
- Sports drinks can be beneficial for individuals who engage in prolonged vigorous physical activity, or those sweating for prolonged hours due to warm to hot temperatures [OK, they have sugar, but recommend them anyway]
I can’t wait to see what the DGAC does with this impressively written document.
Not that it matters, really. Recall: The DGAC submits the research report, but the agencies—USDA takes the lead this time—write the actual guidelines.




 Does this report settle the questions? Hardly. Remember
Does this report settle the questions? Hardly. Remember