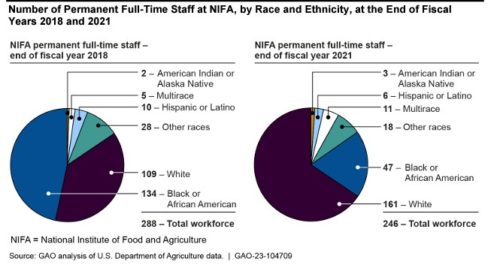
The School Nutrition Association vs. USDA’s nutrition standards
Try as hard as I can, I will never understand why everyone—rich or poor, democrat or republican—isn’t doing everything possibly to make sure that all kids in schools are offered healthy breakfasts and lunches, every day, at no cost.
Children are the future of our country. We need them to be healthy.
That is why I will never understand how anyone could oppose universal school meals and the strongest nutrition standards possible, let alone the people who produce those meals as represented by the School Nutrition Association (SNA).
OK, the SNA strongly encourages partnerships with food and beverage companies. The SNA does not list its donors on iany obvious place on its website, but does list the ones that contribute to its annual meeting. A few years ago, reporters said food companies accounted for half the organization’s revenues.
Perhaps that accounts for the SNA’s long-standing opposition to improving nutrition standards for school meals and the USDA’s latest efforts to do so.
The SNA’s 2023 position paper calls for some useful things: higher reimbursement rates for school meals, universal school meals, reductions in administrative burdens.
But, it also wants: the USDA to drop its new “additional, unachievable rules.”
In February, USDA proposed stricter, long-term nutrition rules. However, 88.8% of school nutrition directors reported challenges
obtaining sufficient menu items (e.g. whole-grain, low-sodium, low-fat options) to meet current standards. Additionally, 97.8% are concerned about the availability of foods to meet the July 2023 transitional sodium limits. To keep students eating healthy school meals, USDA must support school nutrition professionals as they work to maintain current standards.
Briget Huber, writing for FERN, quotes the SNA’s director of media relations.
Additional rules are just not feasible for schools right now…Interim rules cutting sodium more modestly than in the USDA’s new proposal take effect in July, and in a recent survey, SNA members “overwhelmingly” said they were not prepared to meet even those standards…They are very concerned about the availability of foods that meet the targets and are acceptable to students… schools are struggling to staff their kitchens,…They have to compete with local fast-food restaurants and food service establishments that, quite frankly, have a better budget for increasing salaries.
In my experience, schools where personnel believe that healthy meals are important somehow manage to achieve the standards and get the kids to eat the foods. I think the SNA should be supporting them, not undermining them.
As for evidence contrary to the SNA’s position:
- Center for Science in the Public Interest keeps a scorecard on school meals. Its data show much compliance with standards.
- Tufts University researchers find that school meals are healthier than those eaten at home or anywhere else.
- The USDA’s School Nutrition and Meal Cost Study finds most school able to meet the standards and that meals are getting more nutritious.
- Researchers have shown: following passage of the law that improved USDA’s school nutrition standards, its “implementation was associated with a significant decrease in [Body Mass Index] among school-aged youths in the US. The findings suggest that school meal programs represent a key opportunity for interventions to combat the childhood obesity epidemic given the high rates of program participation and the proportion of total calories consumed through school-based meals.
Yes there are financial and logistical difficulties. And yes, kids in school won’t be eating food that is as junky. That’s the point!
The SNA should be leading the country on encouraging schools to serve the healthiest meals possible. That it is not doing so is a disgrace.
Here are the USDA’s infographics (other resources are also available at the USDA’s site):
- Updated Nutrition Standards Posed Challenges but Achieved Underlying Goals
- School Meals Are More Nutritious After Updated Nutrition Standards
- Progress Toward Implementing Updated Nutrition Standards
- The Cost of Producing School Meals Has Increased
- Lunches Consumed From School Are the Most Nutritious
*******
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.