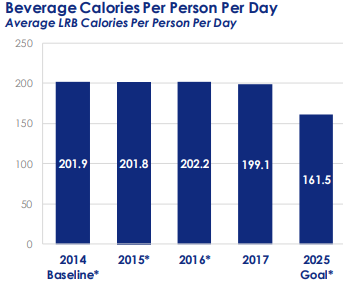
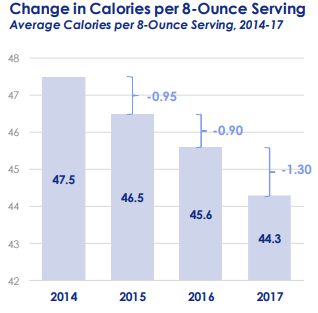
Unsavory Truth came out late last year, but I’m following up by posting recent examples of the issues it covers. Here, for example, is a recent study that caught my eye:
The role of dietary sugars in health: molecular composition or just calories? Philip Prinz. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2019).
A big argument in nutrition right now is whether the metabolic dysfunction that results from excessive consumption of sugars is due to the sugars themselves or to the calories they produce (or, I suppose, to both).
The author who attempted to answer this question conducted a lengthy and detailed review of research on the effects of sugars on obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic conditions . His conclusion:
Current scientific evidence does not support the conclusion that dietary sugars themselves are detrimental to human health and the cause of obesity as well as NCDs [non-communicable— chronic—diseases]. Data from human studies clearly shows that it is the excess amount of calories, also consumed in form of dietary sugars, that promotes obesity and with that favors NCDs. For sucrose, further research is needed in order to evaluate the relevance of its molecular composition, especially in comparison with other macronutrients.
In other words, you don’t have to worry about sugars; just don’t overeat anything.
So, who paid for this?
The paper provides no disclosures of funding or conflicted interests.
But if you click on Philip Prinz, you will see that he is with the Department of Nutritional Sciences, German Sugar Association, Berlin, Germany
Comment
My interpretation of this literature generally favors calories (see my book with Malden Nesheim, Why Calories Count: From Science to Politics). As I see it, when it comes to weight gain, how much you eat matters more than what you eat, especially if your diet is reasonably healthy.
But I would be much more confident in conclusions like these if they came from a researcher whose salary did not depend on producing desirable results for a sugar association.
And everybody would be better off eating less sugar, for reasons of nutritional health, if not necessarily weight.