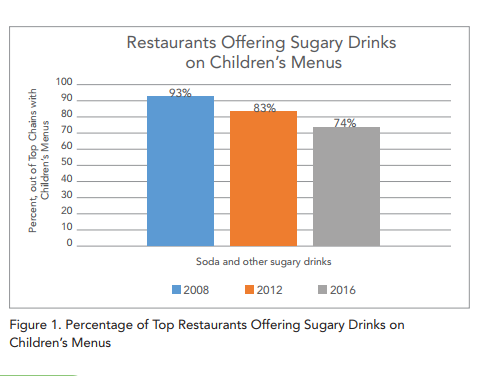
Soda company pouring rights contracts: exposed!
I first wrote about soda company pouring rights contracts in 2000. I also discussed these contracts in Soda Politics: Taking on Big Soda (and Winning).
These contracts are still a big issue, at least at the college level.
A site called MuckRock has just published an analysis of 38 pouring rights contracts, which it obtained through open-records requests from public universities.
Good for them! The contracts make riveting reading.
Coke and Pepsi compete for these contracts and it is easy to understand why. They provide for exclusive sales of the winning company’s products on school campuses.
The companies give the schools money, often in the millions. In return, the schools are required to promote—heavily—the contracted products.
As MuckRock documents, the contracts demand lots of space and exposure for the products. They turn colleges and universities into pushers of sugary beverages. This, at a time when everyone would be healthier avoiding sugary drinks or consuming them in small amounts.
MuckRock posts the contracts so you can read them for yourself.
Is your college not listed? MuchRock says:
Well, we want to expand our survey to your school, too. Help us out by sending us the name of a public college or university, and we’ll submit a request for its alliance in the Battle of the Colas.
This is great investigative reporting. When I wrote my 2000 article, I based it on one contract leaked to me by a school food official appalled by this marketing technique. At the time, Coke and Pepsi were contracting with junior high and elementary schools. Fortunately, they have stopped doing that and are now concentrating on older kids.
That’s some progress, I guess.
Want to get pouring rights off of your campus? Good luck with that. This is a perfect example of money vs. public healh. Guess which is more likely to win.