COP-28, the UN’s climate change conference is happening in Dubai, right now.
I’m trying to make sense of it. For starters, the irony:
But food—the effects of agriculture on climate change (and vice versa) is on its agenda this year—a major big deal.
That’s why a coalition of farmers, communities, business, and philanthropy has issued a call to transform food systems.
Here’s my collection of food-related items.
I. Food Tank’s Danielle Nierenberg is on the job: more than 30 Food Tank partnered events are scheduled.
Once again, four pavilions will be devoted to food systems: Food and Agriculture, led by our partners and friends at FAO, CGIAR, International Fund for Agricultural Development, and The Rockefeller Foundation; Food Systems, spearheaded by the European Union-backed program EIT Food and a variety of other groups including the Food and Land Use Coalition; Food4Climate, organized by a variety of partners—including youth voices—pushing for a more humane and sustainable food system; and the Sustainable Agriculture of the Americas Pavilion facilitated by IICA, bringing together the global north and south across the hemisphere. You can read Food Tank’s coverage of the roadmap, which was announced last year, here.
II. FoodDive: Food system transformation on the menu at COP28
III. Reuters: Countries urged to curb factory farming to meet climate goals
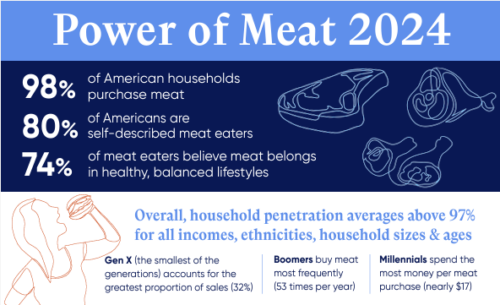
IV. The lunch menu: The summit is featuries roughly two-thirds plant-based menu to highlight the link between greenhouse gas emissions and livestock. But the meat industry is fighting back.
V. DeSmog: Big Meat Unveils Battle Plans for COP28
VI. The Guardian: Plans to present meat as ‘sustainable nutrition’ at Cop28 revealed: Documents show industry intends to go ‘full force’ in arguing meat is beneficial to the environment at climate summit.
VII. The Meat Institute
The Meat Institute and the Protein PACT for the People, Animals & Climate of Tomorrow will highlight animal agriculture’s commitments and progress toward global goals in multiple high-level engagements at the UN Climate Change Conference (COP28) in Dubai November 30-December 12. The Protein PACT has organized or assisted with inviting expert speakers for six panels across five COP28 pavilions, including:
- December 5 panel in the Food Pavilion, co-organized by IICA and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) on the topic of sustainable and healthy livestock production systems
- December 6 panel in the IICA pavilion, organized by the Canadian Alliance for Net-Zero Agri-food on the topic of achieving net zero in agrifood systems
- December 8 panel in the IICA pavilion, organized by the Protein PACT on the topic of principles, practices, and proof for animal agriculture driving climate and food security solutions
- December 9 panel in the IICA pavilion, co-organized by IICA and ILRI on the topic of innovation and investment in livestock systems for climate change adaptation and mitigation
VIII. International Dairy Federation & European Dairy Association side event: How Animal Source Food Nourishes The World In Times of Climate Change.
IX. Vox: There’s less meat at this year’s climate talks. But there’s plenty of bull. Meat and dairy are driving the climate crisis. Why won’t world leaders at COP28 do anything about it?
X. Food Navigator: on The Emirates Declaration. Food is finally at the top table but measurable targets are missing. Over 130 prime ministers and presidents have today signed the Emirates Declaration at COP28 – a first of its kind commitment to adapt and ‘transform’ food systems as part of action on the climate crisis…. Read more
Comment: The Emirates Declaration on Sustainable Agriculture, Resilient Food Systems and Climate Action is the firsr statement out of this meeting. It doesn’t mention fossil fuels (the elephant in this particular room) or meat. But it does propose:
1. Financial and technical support for sustainable solutions, capacity building, infrastructure, and innovations for farmers, fisherfolk, and other food producers.while conserving, protecting and restoring nature.
2. Promoting food security and nutrition.
3. Supporting workers in agriculture and food systems whose livelihoods are threatened by climate change.
4. Strengthening water management .
5. Conserving, protecting and restoring land and natural ecosystems, enhancing soil health, and biodiversity, and shifting from higher greenhouse
gas-emitting practices to more sustainable production and consumption approaches, including by reducing food loss and waste and promoting sustainable aquatic blue foods.
As for how and when?
To achieve these aims – according to our own national circumstances – we commit to expedite the integration of agriculture and food systems into our climate action and, simultaneously, to mainstream climate action across our policy agendas and actions related to agriculture and food
systems.
In the meantime, consider these:
What will it take to stop the impending disaster? This has to be #1 on the advocacy agenda.