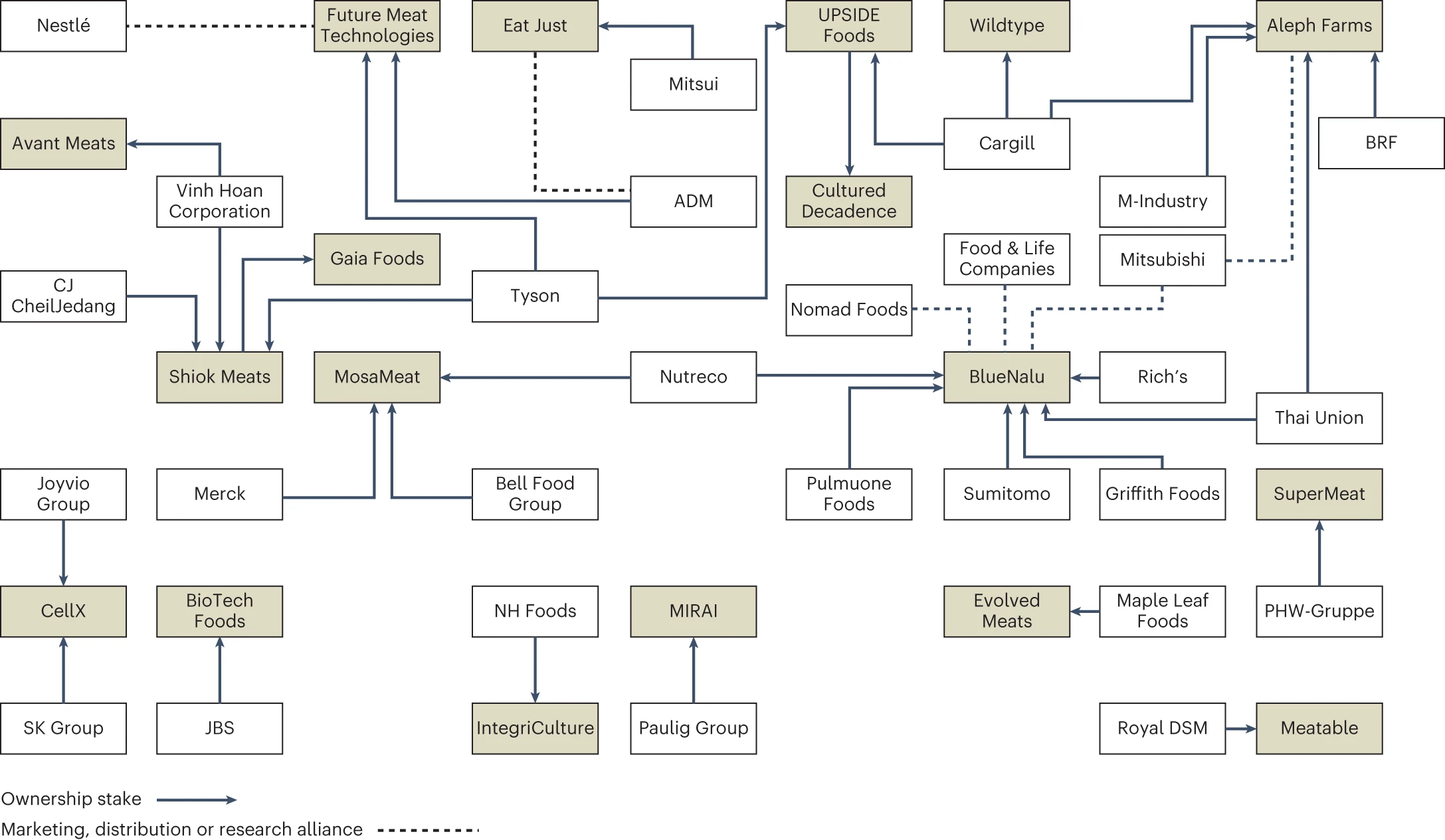
Plant-based meat alternatives: the latest not-good news
Uh oh. Plenty of bad news in the plant-based meat arena.
I. Partnership with health organizations.
The plant-based meat company, Beyond Meat, is partnering with the American Cancer Society to sponsor research on the potential benefits of plant-based meat to cancer preventon.
Beyond Meat, Inc., a leader in plant-based meat, and the American Cancer Society (ACS), today announced a multi-year agreement to advance research on plant-based meat and cancer prevention, as well as to help ACS continue to build the foundation of plant-based meat and diet data collection. The commitment aims to advance the understanding of how plant-based meats contribute to healthy diet patterns and their potential role in cancer prevention and is a crucial step towards long-term research in the plant-based protein field.
Here’s the Cancer Society’s rationale:
Since 2015, the International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified red meat as a carcinogen that increases the risk of colorectal cancer, and recent studies also suggest a possible role of red and/or processed meats in increasing the risk of breast cancer and certain forms of prostate cancer. For years, the American Cancer Society investigators conducted foundational work identifying the link of red and processed meat to cancer…ACS guidelines point to evidence of a significant link between high red and processed meat consumption and an increased risk of colorectal cancer as the primary reason for the recommendation to limit those products.
OK, but research sponsored by a company that stands to benefit from studies showing a benefit of highly processed plant-based meat substitutes?
My prediction: the studies will show benefits.
If the ACS wants such studies, it should fund them on its own.
II. Dirty factories.
Bloomberg News has a report on unclean and unsafe conditions in a Beyond Meat factory.
III. Loss of customers.
The New York Times says Beyond Meat is struggling.
But these days, Beyond Meat has lost some of its sizzle.
Its stock has slumped nearly 83 percent in the past year. Sales, which the company had expected to rise as much as 33 percent this year, are now likely to show only minor growth…In late October, the company said it was laying off 200 people, or 19 percent of its work force. And four top executives have departed in recent months, including the chief financial officer, the chief supply chain officer and the chief operating officer, whom Beyond Meat had suspended after his arrest on allegations that he bit another man’s nose in a parking garage altercation.
What investors and others are debating now is whether Beyond Meat’s struggles are specific to the company or a harbinger of deeper issues in the plant-based meat industry.
IV. Business issues.
The Wall Street Journal reports: “Beyond Meat’s Very Real Problems: Slumping Sausages, Mounting Losses.”
Mr. Brown has said Beyond and other meat-alternative companies are facing challenges as they compete with less expensive real meat at a time of inflation and consumer uncertainty over the health benefits of what many see as highly processed products.
IV. More research needed.
A study looking at the implications of replacing meat with plant-based alternatives makes that point clearly.
See: Santo RE, et al. Considering Plant-Based Meat Substitutes and Cell-Based Meats: A Public Health and Food Systems Perspective. Front. Sustain. Food Syst., 31 August 2020.
Research to date suggests that many of the purported environmental and health benefits of cell-based meat are largely speculative…The broader socioeconomic and political implications of replacing farmed meat with meat alternatives merit further research.
An additional factor to consider is that much of the existing research on plant-based substitutes and cell-based meats has been funded or commissioned by companies developing these products, or by other organizations promoting these products.
Of course we need more research. Don’t we always?
The bottom line: It’s hard to convince people to like fake foods, especially when they are expensive.
Soylent Green, anyone?
***********
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.