Task force on Hunger, Nutrition, Health report: a missed opportunity?
The Task Force on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health released its comprehensive report yesterday.
The report’s purpose is to inform the upcoming White House Conference on Hunger, Nutrition, and Health. If so, it’s going to leave the White House in a quandary.
The report has lots of useful information, beautifully presented, and does all it should on adddressing hunger.
But as I read it, the report, titled Ambitious, Actionable Recommendations to End Hunger, Advance Nutrition, and Improve Health in the United States,” is not nearly ambitious enough when it comes to nutrition and health.
It makes far too many recommendations—30. That’s always a bad sign (too many to do). .
Really, only 2 recommendations are needed. These should establish or expand federal agriculture, food, and nutrition policies to ensure:
- Adequate, affordable food and nutrition for everyone.
- Healthy diets for everyone, meaning those that follow Dietary Guidelines and are largely plant-based, balanced in calories, and low in undesirable fats, sugars, and salt (i.e., ultra-processed foods).
The hunger recommendations do the job: they call for ensuring benefits sufficient to meet households’ basic needs.
But the second? A mess.
Here is the most obvious example [my comments follow] .
Recommendation #9: “Reduce the marketing of foods that do not align with the latest DGA and increase the marketing of foods that align with the latest DGA to children and populations with disproportionate rates of diet-related chronic conditions” [Good! But not through the recommended voluntary methods by industry. That won’t work; it requires legislation]
But here’s Recommendation #25: “Increase the ability of food companies to communicate with consumers about the evidence for healthfulness of certain food products and nutrients.” [Uh oh]
This comes with three action items:
- FDA should expeditiously update its definition of the word “healthy” [good] and incentivize food companies to use the terminology and/or associated symbol in their food packaging and marketing [Yikes!] and increase the proportion of products on the market that meet the “healthy” definition [OK, as long as they are not gaming the system].
- Congress and/or FDA should improve and streamline the process for application, review, approval, and use of health claims and qualified health claims on food packages. [No! If it’s one thing we don’t need, it’s more misleading health claims].
- Congress and/or FDA should create a new process for communicating about foods, nutrients, and other bioactive ingredients that may prevent or treat disease through label claims. [No! We do not need more claims for the benefits of ultra-processed food products].
What’s missing from this report?
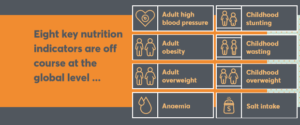
- Anything about ultra-processed foods and their effects on calorie intake and overall health. The term is mentioned once, but only in the context of ‘more research needed’ (Recommendation #19).
- A clear statement of the benefits of soda taxes in reducing consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages. Why isn’t there one? A box explains: “Task Force members voiced diverse perspectives on this topic.”
- A clear statement about making SNAP align with Dietary Guidelines. This is mentioned, but only in the context of pilot research (recommendation #2), and therefore contradicts recommendations #3 and #5. #3: Increase nutrition security by promoting dietary patterns that align with the latest Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA) through federal nutrition programs. #5: Leverage the federal nutrition programs’ power in economic stimulus to support food systems that promote foods that align with the latest DGA.”
- Firm calls on Congress to pass legislation to do what is needed.
What happened? One member of the committee explained to me that its membership included everyone from anti-hunger advocates to food industry representatives, and too many vested interests were at stake. Members could not agree on anything that would make a real difference to policy. Anything substantive met strong resistance.
When it comes to public health policy, which this most definitely is, the food industry has no business being at the table.
This was a recommendation of the 2019 Lancet Commission on the Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change. Read that report. It explains why including the food industry in policy recommendations that might reduce sales is not a good idea.
If I had been a member of this Task Force, I would have called for a minority report on policies for reducing consumption of sugary drinks and ultra-processed foods. But that, of course, is why I’m no longer appointed to such committees.
- Register here for the Webinar hosted by the co-chairs: Wednesday, Aug. 31 at 2:00 p.m. ET.


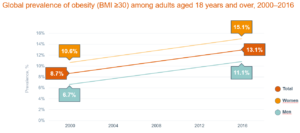
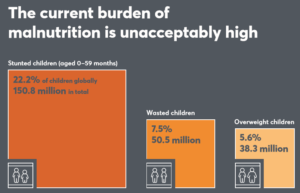 It also deals with adult obesity:
It also deals with adult obesity: