By this time, you have no doubt heard about the Trump Administration’s attempts to stop the World Health Organization from promoting breastfeeding. Incredible but true.
Here is a brief timeline of how this story got out.
May 25 Lucy Sullivan, executive director o 1000 Days (the first 1000 days of life are critical to an infant’s survival) sent out a tweet warning of a battle brewing over breastfeeding at WHO’s World Health Assembly, where countries are negotiating a resolution on infant and young child feeding.
June 7 Amruta Byatnal writes about “A Moment of Reckoning for Nutrition Advocates at the WHA” [World Health Assembly: “Nutrition advocates have accused the U.S. of siding with private sector interests, sparking a controversy over what they assumed would be a routine effort to provide advice on breastfeeding and the use of breast milk substitutes.”
July 8 The New York Times takes the story national: “Opposition to Breast-Feeding Resolution by U.S. Stuns World Health Officials.” The Guardian also publishes an account. These make it clear that the Trump Administration threatened Ecuador to drop its support of breastfeeding. As the Times put it,
The Americans were blunt: If Ecuador refused to drop the resolution, Washington would unleash punishing trade measures and withdraw crucial military aid. The Ecuadorean government quickly acquiesced….The confrontation was the latest example of the Trump administration siding with corporate interests on numerous public health and environmental issues.
Ironically, Russia stepped in and introduced the measure, which passed despite US attempts to block it.
July 9 President Trump sends out a tweet:
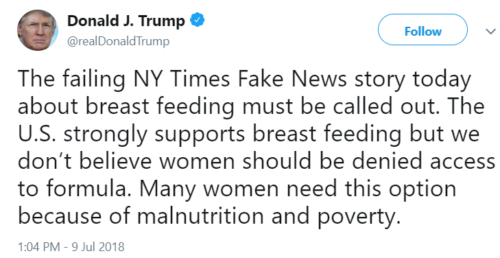
July 9 Alex Azar, Secretary of Health and Human Services, also sends out a tweet, supporting the President: “America has a long history of supporting mothers and breastfeeding around the world and is the largest bilateral donor of such foreign assistance programs. Those unable to breastfeed shouldn’t be stigmatized; they should be equally supported with info and access to alternatives.”
July 9 The New York Times publishes an editorial: “Why Breast-Feeding Scares Donald Trump.” Its answer: “It comes down to public health abroad could hurt American companies’ profits.”
What this is about
Infant formula works for babies, but breastfeeding is demonstrably better. This is especially true for women who cannot afford formula, do not have clean water to dilute the powder properly, or lack refrigeration to store formula properly.
But breastfeeding has a serious political problem: it does not make money for formula companies. As I explained in Waht to Eat:
Infant formulas cause controversy and are endlessly contentious for three important reasons. Formulas are (1) largely unnecessary (most mothers can breast feed their infants), (2) not as perfect as breast milk for feeding babies, and (3) more expensive than breast feeding. Breast milk is nutritionally superior to formula, but from a marketing standpoint it has one serious disadvantage: it is free. Beyond one-time purchases of breast pumps, storage bottles, or special clothing, nobody makes money from it.
Formula companies are happy to pay lip service to “breast is best,” as long as policies do not promote breastfeeding over formula.
This is not the first time the US has taken this position. In 1981, when the United Nations developed the International Code of Marketing of Breast-Milk Substitutes, all of its member countries agreed to abide by the Code except for the United States and South Africa. Eventually, South Africa signed on. The U.S. was the last hold out and did not agree to abide by the Code until 1994. Why not? Because the Code could set a precedent that might adversely affect U.S. corporations.
The Washington Post (“US efforts”) and The Atlantic (“epic battle”) review this history.
The formula industry’s problem
As I also explained in What to Eat, only about 4 million babies are born in the US each year, meaning that the formula market is limited and static. That is why formula companies work so hard to convince mothers that breastfeeding is too difficult, unsanitary, inefficient, and ineffective to continue, and that they would be better off switching to formulas and staying on formulas long past the time when babies should be eating solid foods.
The reactions
My favorites are from
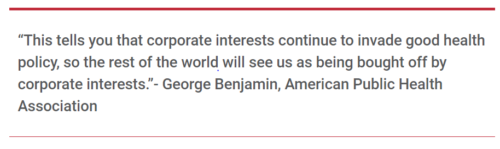
Add this to the growing list of ways the Trump Administration favors corporate interests over public health. Alas.
Additions
Maplight reports:
Three of the largest infant formula companies — U.S.-based Abbott Laboratories, Swiss-based Nestle, and U.K.-based Reckitt Benckiser — have spent $60.7 million lobbying U.S. lawmakers and officials during the last decade….While the New York Times reported that the formula manufacturers didn’t play a visible role in the debate over the WHO resolution, lobbying records show they have a significant Capitol Hill presence that often extends beyond infant nutrition.
Stephen Colbert’s take

 This gives me a chance to point out that Nestlé, the largest food company in the world, is not a relative, fortunately or unfortunately, depending on how you look at it.
This gives me a chance to point out that Nestlé, the largest food company in the world, is not a relative, fortunately or unfortunately, depending on how you look at it.



