Weekend reading: The Lancet / EAT Forum report on healthy and sustainable diets
I’ve saved this for Weekend Reading because it will take a weekend to get through it. The report is a blockbuster: 37 authors, 47 pages, 357 references.

The Lancet commissioned this report from the EAT Forum, which brought together international experts on diet and health (most of whom I do not know) to define unifying dietary principles that best promote will promote the health of people and the planet.
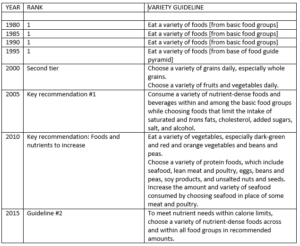
Fortunately, the diet that is best for health is the same diet as is best for the planet. The report defines it on page 5.
To summarize:

This report has many strengths:
- It is researched in depth and is now the reference source for information about needed dietary changes.
- It firmly links dietary health to environmental sustainability.
- Its findings are consistent with many previous reports on diet and health, including that of the 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee DGAC).
- Its messages are unambiguous.
- The summary report is a big help
- The timing is excellent; the 2020 Dietary Guidelines advisory committee, if it ever gets appointed, will have to pay close attention to the science reviewed in this report.
- It focuses on food, not nutrients (these meals meet the standards of recommended diets).
 Does this report settle the questions? Hardly. Remember the fuss over sustainability (the “S-word?”) in the 2015 report of the DGAC?
Does this report settle the questions? Hardly. Remember the fuss over sustainability (the “S-word?”) in the 2015 report of the DGAC?
- The meat industry does not like advice to eat less meat.
- The dairy industry doesn’t like it either. Its trade associations emphasize its nutritional value and source of livelihood for a billion people.
- The food industry has lots of complaints.
There is lots to read and think about here. Enjoy!
- The Lancet home page for the report (includes slides, links)
- The Lancet editorial accompanying the report
- The EAT Forum home page for the report (information about EAT, the launch, the commission members, etc)
- The EAT Forum summary report