The 2025-2030 Dietary Guidelines: Some preliminary speculation
As I noted last May, I get asked all the time about what they will say, but have no inside information. But this may be a good time to go over the clues.
The process
- A scientific advisory committee reviews the research and writes a report. This was released in December.
- Unspecified (to date) people in USDA and HHS write the guidelines.
The promises
- They will come out “hopefully early fall” (this did not happen)
- Now, according to Reuters, the new dietary guidelines will be released some time in December.
What they won’t say
- They will not continue the tradition of “leftist ideology” [I think this must mean plant foods]
- They will not promote seed oils (RFK Jr prefers beef tallow).
- They will not promote sugar; RFK Jr says sugar is poison. [But declared a MAHA Win for Coca’ Cola’s replacement of high fructose corn syrup with cane sugar]
- They won’t say anything about sustainability [anything about climate change is forbidden]
What they will be about
[According to Reuters] Kennedy said the new guidelines would change the kind of food served to military service members and children in schools, but gave no details on the new recommendations.
“If we want to solve the chronic disease crisis, we have to tackle obesity,” Kennedy said. “Obesity is the number one driver of chronic disease,” he said, adding that 50% of the adult U.S. population was obese or overweight, driving costs up for diabetes care and cardiac diseases.
What they might say
Beef
- In its Plan to Fortify the Beef Industry, the USDA says the 2025–2030 Dietary Guidelines will “encourage protein as the foundation for every meal.”
- In an announcement to ranchers, USDA quotes RFK Jr, “we are restoring whole foods as the foundation of the American diet and ending the decades-old stigma against natural saturated fat in beef and dairy products. We will strengthen America’s ranching industry so families can choose nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods.”
Dairy
In a news conference, officials gave some clues.
We are going to be there for the dairy industry…our agencies are about to release more dietary guidelines in the next several months that will elevate those products to where they ought to be…There’s a tremendous amount of emerging science that talks about the need for more protein in our diet, and more fats in our diet, and there’s no industry that does that better than this industry.
Speculation
When RFK Jr first talked about the new guidelines, he said they would ignore the scientific advisory committee report and would be simple, short (5 pages), easy to understand, and out by September. I’m guessing that the conflict between the science and ideology is proving more difficult to resolve than anticipated.
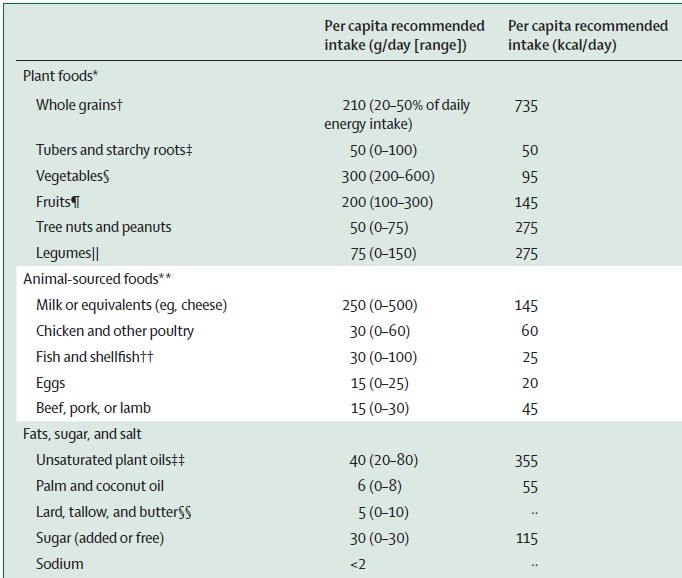
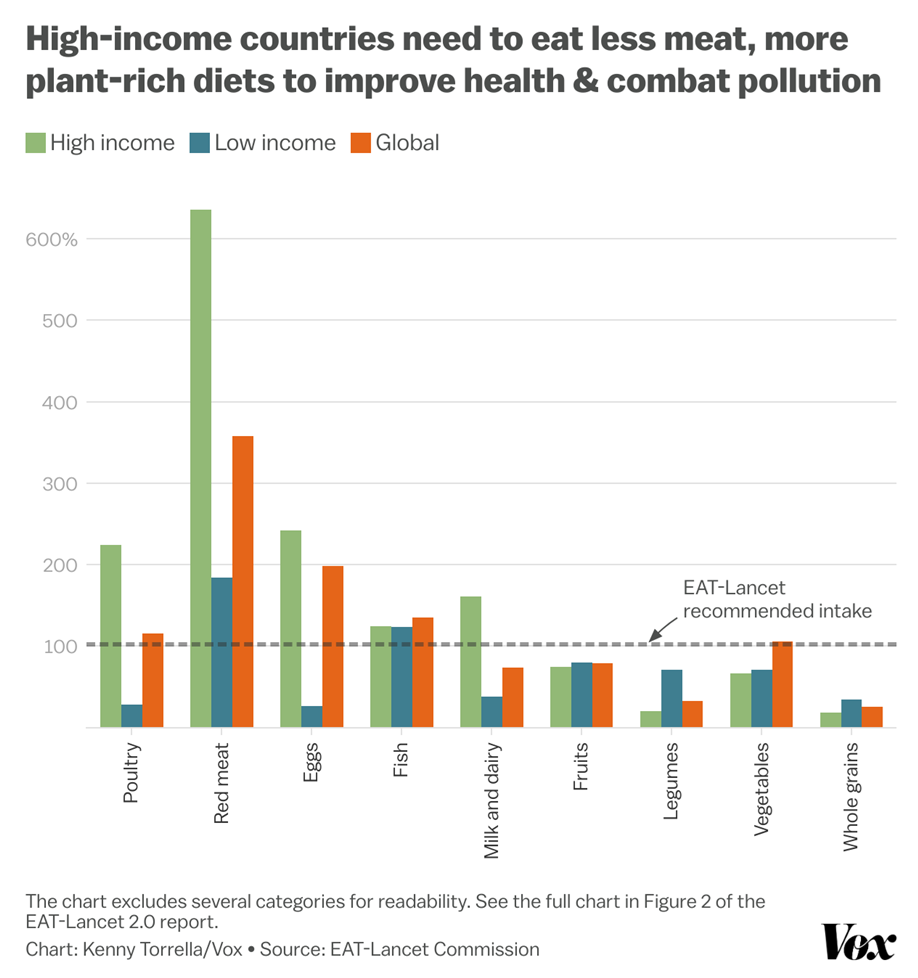
The science continues to argue for a largely (but not necessarily exclusively) plant-based diet, reduced in meat and ultra-processed foods from current levels. RFK Jr initially talked about the need to reduce intake of ultra-processed foods, but the second MAHA report merely asked for a definition.
This administration seems obsessed with protein, a nutrient already in excess in US diets.
If it wants to do something about obesity, it needs the guidelines to suggest ways to reduce calories. Nobody has mentioned that word so far.
As I keep saying, I can’t wait to see what the new guidelines will look like. Stay tuned.