According to USDA,
Federal Milk Marketing Orders (FMMOs) establish certain provisions under which dairy processors purchase fresh milk from dairy farmers supplying a marketing area. ..A marketing area is generally defined as a geographic area where handlers compete for packaged fluid milk sales…Federal orders serve to maintain stable marketing relationships for all handlers and producers supplying marketing areas, thus facilitating the complex process of marketing fresh milk.
USDA has a brochure on how the program works.
FMMOs establish monthly uniform prices paid to farmers by first classifying milk by its end use. The FMMO then pools the value of that milk and shares that value among the farmers participating on that marketing order. Pooling allows farmers to receive the uniform price of all milk in the pool regardless of what end product their milk was used for. In this way, pooling makes a farmer’s payment independent of how the milk was used.
Got that?
Here are the current milk marketing regions:
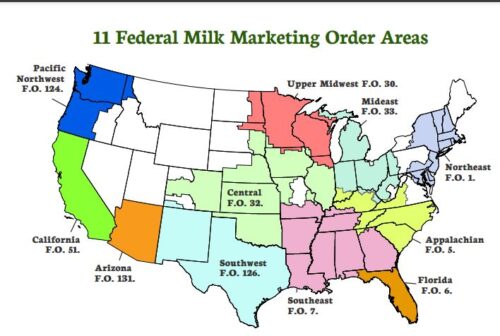
I have to confess that Milk Marketing Orders are beyond me, but I am trying . I understand the basics. They are supposed to do three things: (1) establish minimum prices paid to dairy farmers, (2) ensure payments are accurate and timely, and (3) provide market information.
To try to understand how this works, I subscribe to AgriPulse News (“Providing balanced coverage of the food, fuel, feed, and fiber industries”).
From AgriPulse, I learned:
After more than two years of discussion and more than 130 meetings, the National Milk Producers Federation Board of Directors unanimously endorsed a comprehensive plan to correct shortcomings exacerbated during the pandemic regarding pricing regulations for milk.
Among the proposed changes, NMPF called for a return to the “higher of” Class 1 mover that was changed in the last farm bill.
NMPF also recommended that USDA update make allowances and review them every two years. Make allowances are based on estimates of what it costs to convert a hundredweight of raw milk into commodity dairy products such as cheese, butter, whey and nonfat dry milk.
NMPF plans to submit its proposal to USDA for a hearing and a potential producer referendum on the order’s modernization yet this year. The International Dairy Foods Association previously said it would request a hearing only on the make allowances request.
I looked at the comprehensive plan. Here are NMPF’s requested changes to the Federal Milk Marketing Order System:
- Returning to the “higher of” Class I mover;
- Discontinuing the use of barrel cheese in the protein component price formula;
- Extending the current 30-day reporting limit to 45 days on forward priced sales on nonfat dry milk and dry whey to capture more exports sales in the USDA product price reporting;
- Updating milk component factors for protein, other solids and nonfat solids in the Class III and Class IV skim milk price formulas;
- Developing a process to ensure make-allowances are reviewed more frequently through legislation directing USDA to conduct mandatory plant-cost studies every two years;
- Updating dairy product manufacturing allowances contained in the USDA milk price formulas; and
- Updating the Class I differential price system to reflect changes in the cost of delivering bulk milk to fluid processing plants.
For starters, what is a “Class I mover?” For this, I need help.
The USDA classifies milk into four categories:
CLASS I – Milk used for beverages including eggnog and ultra-high temperature (UHT) milk.
CLASS II – Milk used for soft products. This includes cottage cheese, ricotta cheese, pot cheese, Creole cheese, milk shake and ice milk mixes, frozen desserts, aerated cream, frozen cream, sour cream, half-n-half, yogurt, custards, puddings, pancake mixes, batter, buttermilk biscuit mixes, infant or dietary formulas packaged in hermetically sealed containers, candy, soup and bakery products for general distribution to the public including sweetened condensed milk used for manufacture of aforesaid products, and fluid cream or any product containing artificial fat or fat substitutes that resemble fluid cream.
CLASS III – Milk used in the manufacture of cream cheese and other spreadable cheeses, and hard cheese of types that may be shredded, grated, or crumbled. It also includes plastic cream, anhydrous milkfat, and butteroil.
CLASS IV – Milk used to produce butter, any milk product in dry form and evaporated or sweetened condensed milk in a consumer-type package.
But a Class I mover? I cannot find a definition, although I can easily find examples of how it’s used.
The Federal Milk Marketing Order (FMMO) advanced Class I base price hit another eight-year high in March, but the change in the Class I mover formula implemented in 2019 reduced what might have been an even higher price paid to producers.
Announced by the USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service on Feb. 16, the March I base price is $22.88 per hundredweight (cwt), up $1.24 from February 2022 and $7.68 more than March 2021. It’s also the highest since November 2014.
At $3.12 per cwt, the difference between the advanced Class III skim milk pricing factor ($10.59 per cwt) and the advanced Class IV skim milk pricing factor ($13.71 per cwt) grew substantially. That means producers will see a negative impact using the “average-of plus 74 cents” Class I mover compared to the old “higher-of” formula.
Based on Progressive Dairy calculations, the Class I mover calculated under the higher-of formula would have resulted in a Class I base price of $23.67 per cwt, 79 cents more than the price determined using the average-of plus 74 cents formula. That difference is up from 51 cents per cwt in February.
I give up. If anyone can explain this to me, please do.
This is what you are up against if you want to understand why milk prices are rising at grocery stores.
*******
For 30% off, go to www.ucpress.edu/9780520384156. Use code 21W2240 at checkout.