Industry policy influence of the week: meat and dairy vs. climate change
Thanks to Sinead Boylan in Australia for alerting me to this paper about the influence of the meat and dairy industries on climate change policy. The authors are Environmental Science colleagues at NYU.
The Study: The climate responsibilities of industrial meat and dairy producers. Oliver Lazarus & Sonali McDermid & Jennifer Jacquet. Climatic Change (2021) 165:30.
Method: The authors examined the role of 35 of the world’s largest meat and dairy companies in actions related to preventing climate change. But in particular, it investigated “the transparency of emissions reporting, mitigation commitments, and influence on public opinion and politics of the 10 US meat and dairy companies.”
Its overall conclusion: “all 10 US companies have contributed to efforts to undermine climate-related policies.”
Through a questionnaire, it found (these are direct quotes):
- All 10 US companies have contributed to research that minimizes the link between animal agriculture and climate change (Q11). Three companies—Tyson, Cargill, and Smithfield—have contributed directly to what Brulle (2014) called “climate change countermovement organizations” or organizations that have minimized the link between agriculture and climate change (Q13).
- Four companies—Tyson, National Beef, Smithfield, and Hormel—have each made statements linking climate change regulation with potentially harming their profitability, either in an SEC form or in an annual report (Q17…).
Through researching OpenSecrets
- Nine of the 10 companies have spent at least $600,000 on lobbying activities since 2000, with five of those companies spending over $14 million each…Tyson has spent the most on lobbying—$25 million—over the last two decades.
- Cargill has spent $21.5 million; Smithfield Foods, $21 million; Dean Foods, $16 million; and Dairy Farmers of America, $14 million….
- Combined, the companies have spent a total of $109 million on lobbying activities since 2000.
- The other nine US-based companies [the tenth, Koch Foods, did not report] have spent a combined $26 million on political campaigns since 2000.
- Dairy Farmers of America has spent the most, at $6.3 million since 2000. California Dairies has spent $5 million; Dean Foods, $4.3 million; Cargill, $4 million; and Tyson, $3.2 million.
- Since 2000, Tyson has spent more on Republican candidates in every election cycle but one, and a similar pattern was observed for most of the companies examined here.
- US meat and dairy companies act collectively…Together, six of these [trade] groups—the National Cattlemen’s Beef Association, the National Pork Producers Council, the North American Meat Institute, the National Chicken Council, the International Dairy Foods Association, and the combined expenses of the American Farm Bureau Federation and its state groups—have spent nearly $200 million in lobbying since 2000, lobbying yearly on climate related issues like cap-and-trade, the Clean Air Act, and greenhouse gas regulations and reporting rules.
- A recent sustainability report published by the US pork industry noted that “pork production contributes just 0.46% of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere” (Pork Checkoff 2020).
- In 2019, the National Cattlemen’s Beef Association published a 21-part series, “Tough Questions About Beef Sustainability,” that, among other things, claims US beef production accounted for just 1.9% of total US emissions in 2014 (Beef Research 2019)
Their analysis also suggests: “the level of influence generally corresponded with emissions. Tyson, for example, is the largest emitter of the 10 US companies. Tyson received the highest total influence score in response to our 20 questions at 15, tied with National Beef Packing Company, the fourth highest emitter.”
Overall: “In the case of the USA, our analysis provides evidence to suggest that the 10 largest meat and dairy companies have worked to frame the conversation, influence climate-related policies, and minimize the link between animal agriculture and climate change.”
Comment: This issue matters because animal agriculture is estimated to contribute 14.5% of greenhouse gas emissions. This, and industry behavior around this issue, is a reason why sustainability needs to be part of Dietary Guidelines, and “eat less meat” is good dietary advice for people in industrialized economies.


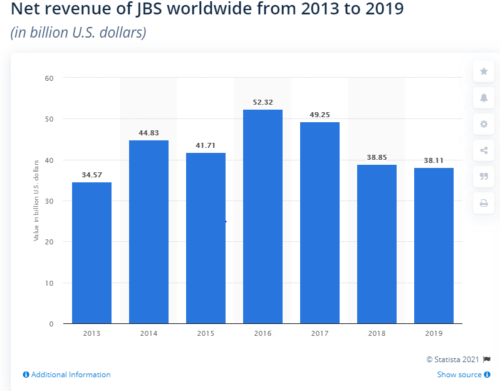

 Why does this matter? Here, for example, is
Why does this matter? Here, for example, is