Conflicted interests: obesity drugs, alcohol, clinical trials
DRUGS
Here’s the headline: Maker of Wegovy, Ozempic showers money on U.S. obesity doctors
Drugmaker Novo Nordisk paid U.S. medical professionals at least $25.8 million over a decade in fees and expenses related to its weight-loss drugs, a Reuters analysis found. It concentrated that money on an elite group of obesity specialists who advocate giving its powerful and expensive drugs to tens of millions of Americans.
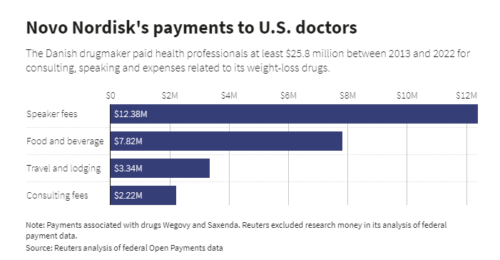
What’s extraordinary about this situation is the amounts. Some doctors got millions.
This account follows one about similar efforts in the UK: Revealed: experts who praised new ‘skinny jab’ received payments from drug maker.
The drug giant behind weight loss injections newly approved for NHS use spent millions in just three years on an “orchestrated PR campaign” to boost its UK influence. As part of its strategy, Novo Nordisk paid £21.7m to health organisations and professionals who in some cases went on to praise the treatment without always making clear their links to the firm, an Observer investigation has found.
Novo Nordisk knew what it was doing, and its efforts (presumably legal) are certainly paying off.
ALCOHOL
The headline: Scientists in Discredited Alcohol Study Will Not Advise U.S. on Drinking Guidelines: Two researchers with ties to beer and liquor companies had been named to a panel that will review the health evidence on alcohol consumption. But after a New York Times story was published, the panel’s organizers decided to drop them.
Five years ago, the National Institutes of Health abruptly pulled the plug on an ambitious study about the health effects of moderate drinking. The reason: The trial’s principal scientist and officials from the federal agency’s own alcohol division had solicited $60 million for the research from alcohol manufacturers, a conflict of interest and a violation of federal policy.
I wrote about that in a previous post.
I’m told by people in the know that I should not be too hard on the scientists. NIH told them it would not fund the study and they should get the funding from industry. If true, that is unfortunate.
For sure, NIH is not interested in nutrition research except for genetically based “Precision” nutrition aimed at individuals. That leaves population studies out of the picture. Unfortunate, indeed.
CLINICAL TRIALS
The study: Industry Involvement and Transparency in the Most Cited Clinical Trials, 2019-2022
Among 600 clinical trials with a median sample size of 415 participants:
- 409 (68.2%) had industry funding
- 303 (50.5%) were exclusively industry-funded
- 354 (59.0%) had industry authors
- 280 (46.6%) involved industry analysts
- 125 (20.8%) were analyzed exclusively by industry analysts.
Among industry-funded trials:
- 364 (89.0%) reached conclusions favoring the sponsor.
Industry involvement in research in general and in nutrition research in particular deserves close scrutiny and much skepticism.
Drug companies are required to do research and to find their own funding. That is not true of nutrition.
Everyone should be lobbying for more independent funding for nutrition research.