Food system reports #2: the deluge
As I mentioned yesterday, everyone seems to be doing reports on food systems—a deluge. Here are the most recent ones I’ve collected.
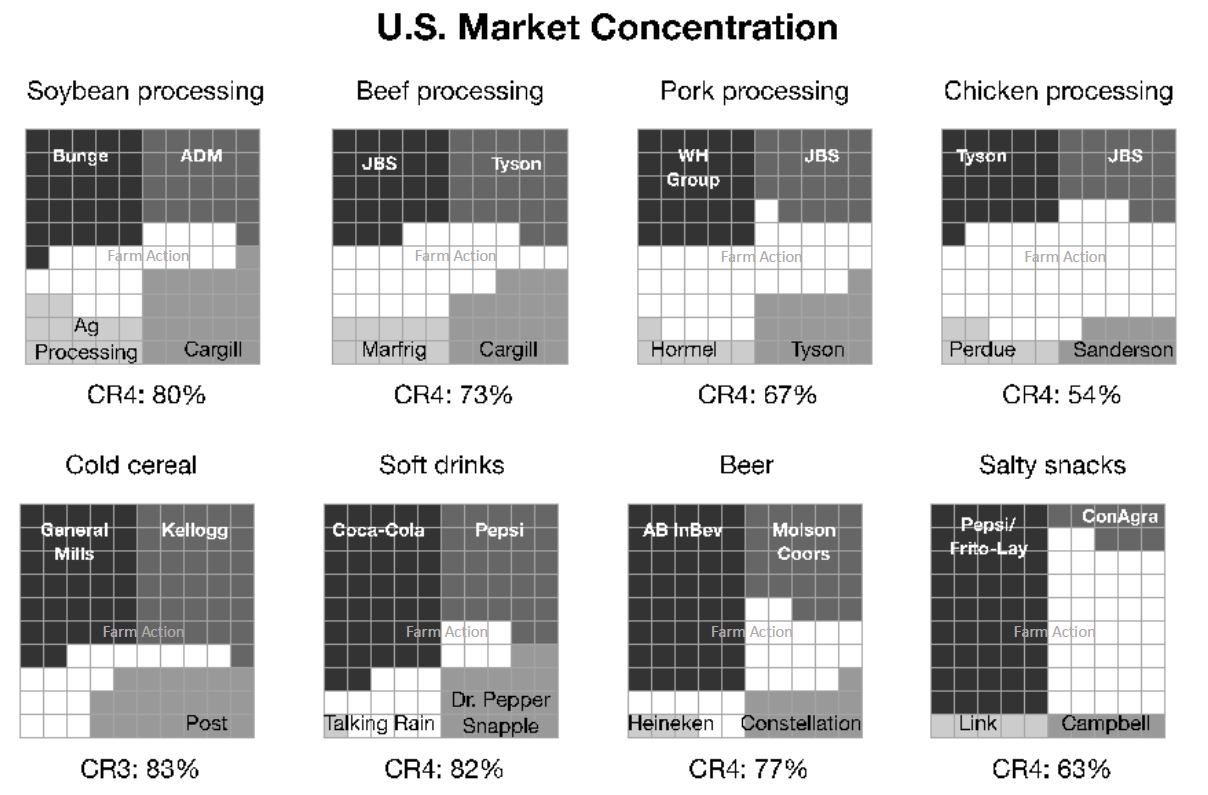
Food and Water Watch: Well-Fed: A Roadmap To A Sustainable Food System That Works For All
The report outlines the alarming degree of corporate consolidation in the food industry and its impact on consumers and small farms. For example:
- 83 percent of all beef is produced by just four processing companies;
- 65 percent of consumer grocery market share is held by just four retailers; and
- 67 percent of crop seed market share is held by just four corporations.
Global Alliance for the Future of Food: Beacons of Hope: Stories of Food Systems Transformation During COVID-19
Building on a program of work launched in 2019 — “Beacons of Hope: Stories of
Transformation” — this short report shares stories of food systems initiatives and the
people who responded to the COVID-19 pandemic with creativity, adaptability, and resilience.
Global Alliance for the Future of Food: How to Transform Food Systems: 7 Calls to Action
The Global Alliance advocates for increased systems-based research into the future of food and positive food environments that are adapted to meet regional conditions and cultural contexts. We also call for transformed governance and decision-making, with additional investment and support for agroecology and regenerative approaches, and excluding harmful subsidies and incentives.
World Resources Institute: Food Systems at Risk: Transformative Adaptation for Long-Term Food Security
Food security, people, climate. These three words are inextricably linked; changes to one will inevitably affect the others. As climate change threatens food-producing regions, what changes are needed to feed a growing population? How can we shift food systems to better adapt to the changing climate? More explicitly, how can policymakers help hundreds of millions of small-scale agricultural producers to enhance food security and improve livelihoods despite the challenges that climate change brings?
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development): Agricultural Policy Monitoring and Evaluation 2021: Addressing the Challenges Facing Food Systems
This annual report monitors and evaluates agricultural policies in 54 countries, including the 38 OECD countries, the five non-OECD EU Member States, and 11 emerging economies. The report includes country specific analysis based on up-to-date estimates of support to agriculture that are compiled using a comprehensive system of measurement and classification – the Producer and Consumer Support Estimates (PSE and CSE) and related indicators. This year’s report focuses on policy responses to the COVID-19 pandemic and analyses the implications of agricultural support policies for the performance of food systems.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN): Food Systems and Nutrition: Handbook for Parliamentarians
Parliamentary action is fundamental to securing the right to adequate food for all. Parliamentarians guide and oversee public-sector policies and budget allocations towards transforming food systems that deliver healthy diets for all. Our vision for this handbook is to provide parliamentarians with practical guidance
to support legislative processes that prioritize nutrition. We look forward to promoting this handbook – together with governments, other international organizations, civil society and other stakeholders – as a tool to facilitate efforts that will accelerate progress towards the SDGs. [Sustainable Development Goals].
Committee on World Food Security (CFS)‘s High Level Panel of Experts (HLPE) on Food Security and Nutrition: Promoting Youth Engagement and Employment in Agriculture and Food Systems
A new UN report on youth and agriculture underscores the urgent need to make agri-food systems more appealing to young people to secure the future of global food security and nutrition. The panel provides independent, scientific analyses and advice to the CFS, an inclusive international and intergovernmental platform for all stakeholders to work together on food security and nutrition for all.