Enjoy the holiday!


The FDA is once again asking food companies to voluntarily reduce the sodium in their products.
It says that 40% of food categories have done just that.
Prior to 2021, consumer intake was approximately 3,400 milligrams per day on average, far higher than the limit recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans of 2,300 milligrams per day for those 14 years and older.
If finalized, the new set of voluntary targets would support reducing average individual sodium intake to about 2,750 milligrams per day. This reduction is approximately 20% lower than consumer intake levels prior to 2021.
it has published a report on this progress.
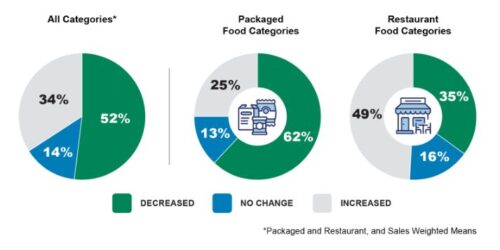
A quick reminder: salt is 40% sodium. The Dietary Guidelines upper limit target of 2300 mg/day sodium means nearly 6 grams of salt per day, or 1.5 teaspoons.
As for why this matters, Sodium Reduction Is A Proven Strategy That Saves Lives—More Work Is Needed To Hold Industry Accountable.
In 2016, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) embarked on a sodium reduction strategy, only to meet repeated political hurdles…there has been little industry engagement, minimal public reporting, and no consequences if targets are not achieved.
Salt reduction across the entire food supply is the only measure that will help people reduce sodium intake. This issue has been around for a long time.
Voluntary reduction is nice, but does not go nearly far enough and it can always be reversed.
The FDA could and should do more.
OK, granted. Political opposition to salt reduction is fierce—if foods aren’t salty enough, people might not buy them.
But the FDA also has a long history of protection of commercial interests, which it claims it cannot share because it is obliged to protect trade secrets. It’s time for that to change too.
I came across this provocative headline in Medium (to which I subscribe): Red Lobster was killed by private equity, not Endless Shrimp.
I knew that Red Lobster had filed for bankruptcy and that its all-you-can-eat shrimp were being blamed for it lack of profitability.
Not at all, Cory Doctorow explains. Blame corporate greed.
Ten years of being bled out on rents and flipped from one hedge fund to another has killed Red Lobster…The supplier who provided Red Lobster with all that shrimp is Thai Union. Thai Union also owns Red Lobster. They bought the chain from Golden Gate Capital, last seen in 2014, holding a flash-sale on all of Red Lobster’s buildings, pocketing billions, and cutting Red Lobster’s earnings in half.
…Thai Union continued to bleed Red Lobster, imposing more cuts and loading it up with more debts financed by yet another private equity giant, Fortress Investment Group. That brings us to today, with Thai Union having moved a gigantic amount of its own product through a failing, debt-loaded subsidiary, even as it lobbies for deregulation of American fisheries, which would let it and its lobbying partners drain American waters of the last of its depleted fish stocks.
Healthcare (a disaster), he says, is a “pretty good model for understanding what happened to Red Lobster:”
monopoly power and monopsony power begat more monopolies and monoposonies in the supply chain. Everything that hasn’t consolidated is defenseless: diners, restaurant workers, fishermen, and the environment…places [like Red Lobster] are easy pickings for looters because the people who patronize them have little power in our society — and because those of us with more power are easily tricked into sneering at these places’ failures as a kind of comeuppance that’s all that’s due to tacky joints that serve the working class.
As he says, it’s not a pretty story. But an increasingly common one, alas.
At last, a presidential candidate interested in food.
The Harris-Walz agenda aims to lower costs for Americans, food costs among them.
Vice President Harris and Governor Walz will work to enact a plan in their first 100 days to go after bad actors to bring down Americans’ grocery costs and keep inflation in check. They will work with Congress to:
- Advance the first-ever federal ban on price gouging on food and groceries;
- Set clear rules of the road to make clear that big corporations can’t unfairly exploit consumers to run up excessive profits on food and groceries.
- Secure new authority for the FTC and state attorneys general to investigate and impose strict new penalties on companies that break the rules.
Furthermore,
Vice President Harris will also direct her Administration to crack down on unfair mergers and acquisitions that give big food corporations the power to jack up food and grocery prices and undermine the competition that allows all businesses to thrive while keeping prices low for consumers.
And her plan will support smaller businesses, like grocery stores, meat processors, farmers, and ranchers, so those industries can become more competitive….More competition means lower prices for you and your families.
Unfair mergers? Mars had just proposed to buy Kellanova, and I discussed the Kroger-Albertson’s proposed merger yesterday.
At a campaign event in North Carolina, Vice President Kamala Harris again discussed food prices.
A loaf of bread costs 50 percent more today than it did before the pandemic. Ground beef is up almost 50 percent. Many of the big food companies are seeing their highest profits in two decades. And while many grocery chains pass along these savings, others still aren’t.
…My plan will include new penalties for opportunistic companies that exploit crises and break the rules, and we will support smaller food businesses that are trying to play by the rules and get ahead.
…We will help the food industry become more competitive, because I believe competition is the lifeblood of our economy. More competition means lower prices for you and your families.
Good, but these are campaign promises that necessarily depend on Congressional support.
…it’s unlikely Democrats will have the votes to pass price-gouging legislation in Congress. Her proposal essentially mirrors a bill from Democratic Sens. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.), Bob Casey (D-Pa.) and Tammy Baldwin (D-Wis.) that has stalled amid GOP opposition.
And Harris’ pitch, which includes giving the FTC more resources to investigate major acquisition deals in the food sector, would need GOP buy-in so Democrats can swing extra FTC resources via spending fights in Congress.
The food industry, of course, protests.
The Food Industry Association blames higher prices on inflation.
The National Grocers Association says its profit margins are already too thin.
I have no idea how any of this will play out, but it’s terrific to see food issues on the agenda.
Recall that the large grocery chain, Kroger, proposed a couple of years ago to acquire another large grocer, Albertsons, for about $25 billion.
The FTC did not think this was a good idea. It FTC filed a suit to prevent the proposed merger on the grounds that it would make the US supermarket landscape even less competitive than it already is. It would be likely to raise prices for consumers, reduce wages for employees, and (as I’ve written previously) lead to the closure of many stores.
Kroger is fighting back. It filed an injunction arguing that blocking the merger violates the constitution.
In its news release, Kroger said
“The merger between Kroger and Albertson’s is squarely focused on ensuring we bring customers lower prices starting day one while securing the future of good-paying union jobs,” said Rodney McMullen, Kroger Chairman and CEO. “We stand prepared to defend this merger in the upcoming trial in federal court – the appropriate venue for this matter to be heard – and we are asking the Court to halt what amounts to an unlawful proceeding before the FTC’s own in-house tribunal.”
In the meantime, BIG, a newsletter on the politics of monopoly power, reports
After two years of investigations and negotiations over court logistics, next week, the Federal trial for the $24 billion Kroger-Albertsons supermarket merger begins. And this one’s really bitter, with new revelations emerging a few days ago from the Federal Trade Commission that a group of Albertsons executives, including CEO Vivek Sankaran, have been deleting text messages relevant to the trial that the court ordered them to preserve. That’s a big legal no-no.
A big legal no-no indeed. This from the FTC’s complaint (references omitted)
On January 17, 2024, the FTC requested a detailed accounting from Albertsons about how responsive documents were lost and what efforts had been taken to recover lost documents. Albertsons did not respond for nearly four months. When they finally responded, they detailed efforts to recover deleted messages from Mr. Broderick’s and Vivek Sankaran’s phones. . Although Albertsons was able to recover approximately 70 text messages from Mr. Sankaran’s phone, further efforts proved unsuccessful…For months, Plaintiffs have tried to seek information about the extent to which Albertsons’ text messages were deleted, obtaining a court order in the Administrative Adjudication requiring production of texts from potential trial witnesses, and raising repeated inquiries about inexplicably missing documents.
This is what the USDA says consolidation in the grocery industry looks like now. The proposed merger will only add to monopoly power int he grocery industry. For the record, Walmart accounts for about 25% of grocery sales int he US.
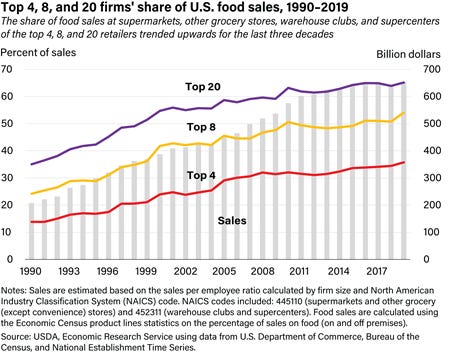
Is the Kroger-Albertson’s merger likely to be good for the public? The FTC does not think so and neither do I.
Nutrients, a journal that requires authors to pay CHF 2900 ($3400) for their articles, does publish the most amazing studies, ostensibly peer-reviewed (I’ve heard mixed things about its process). This journal is a source for many of my Monday posts, each more creative than the next.
This is a good one.
Sourdough Bread with Different Fermentation Times: A Randomized Clinical Trial in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Pérez-Vega KA, Sanllorente A, Zomeño M-D, Quindós A, Muñoz-Martínez J, Malcampo M, Aldea-Perona A, Hernáez Á, Lluansí A, Llirós M, et al.. Nutrients. 2024; 16(15):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152380
Rationale: The Mediterranean diet, featuring sourdough bread, shows promise in managing metabolic syndrome.
Method: In a double-blind clinical trial, participants randomized to consume either Elias Boulanger® long-fermentation (48 h) sourdough bread (EBLong) or Elias Boulanger® short-fermentation (2 h) sourdough bread (EBShort) over a two-month period.
Results. EBShort bread was effective in reducing some inflammation markers.
Conclusion. The consumption of sourdough bread may offer potential benefits in reducing inflammation markers in individuals with metabolic syndrome; however, longer fermentation times did not show additional benefits.
Conflicts of interest: “I.E. and N.EM. were employees of Elias–Boulanger and received funding from RTC-2017-6467-2 program. They had no role in the collection, analyses, and interpretation of data or in the decision to publish the results. The rest of the authors declare no conflicts of interest.”
Comment: I’ll bet they didn’t. Sourdough bread is responsible for the benefits of the Mediterranean diet? That’s news to me. The bread is healthier if its fermented for a shorter time? Also news.
The paper does not describe the taste or texture of the bread.
Thus, the underlying purpose of this study must be to give Elias-Boulanger an excuse to cut down on fermentation time and claim the cheaper, ultra-processed bread is healthier. Count me as dubious, on taste grounds alone.
But isn’t this a great example of marketing research in action? You can’t make this stuff up.
ADDITION
A reader points out that Nutrients is not alone in requiring Article Processing Charges (APCs) for open-access publication. Prestigious journals charge much more.
Susan Greenhalgh. Soda Science: Making the World Safe for Coca-Cola. University of Chicago Press, 2024.

This terrific book picks up where I left off with Soda Politics: Taking on Big Soda (and Winning) (2015) and Unsavory Truth: How the Food Industry Skews the Science of What We Eat (2018).
Susan Greenhalgh’s focus, however, is on ILSI, the International Life Sciences Institute (now renamed the Institute for the Advancement of Food and Nutrition Sciences). ILSI is a classic industry front group, It was created originally by Coca-Cola to make sure science promoted corporate interests. It is funded by big food companies. It positions itself as an independent think tank. Hence: front group.
Soda Science documents how ILSI, working through personal connections (guanxi) at the Chinese Ministry of Health, convinced the Chinese government to target obesity prevention measures at physical activity (“move more”), rather than diet (“eat less,” or “eat better”).
The first half of the book tells the story of ILSI’s role in the Global Energy Balance Network, a group outed as funded by Coca-Cola (I wrote about this in 2015, particularly here, here, and here in The Guardian).
The second half gives an intimate, first-hand account of how science politics works in China.
Greenhalgh is a distinguished anthropologist. She retired from Harvard as as the John King and Wilma Cannon Fairbank Research Professor of Chinese Society (she is an expert on China). She uses social science methods—interviews and qualitative research as well as document review—to study this particular example of soda politics.
The story she tells here is fascinating in its own right and a great read.
It also makes one other point: social science methods are really useful in getting information unavailable any other way.
I say this because bench scientists tend to look down on qualitative research and consider it non-research. I disagree. I think qualitative research is essential, and has plenty to contribute. This book is a great example of why.
While I’m on the topic of AI—a hot issue in the food business—here are a few items I’ve collected recently.