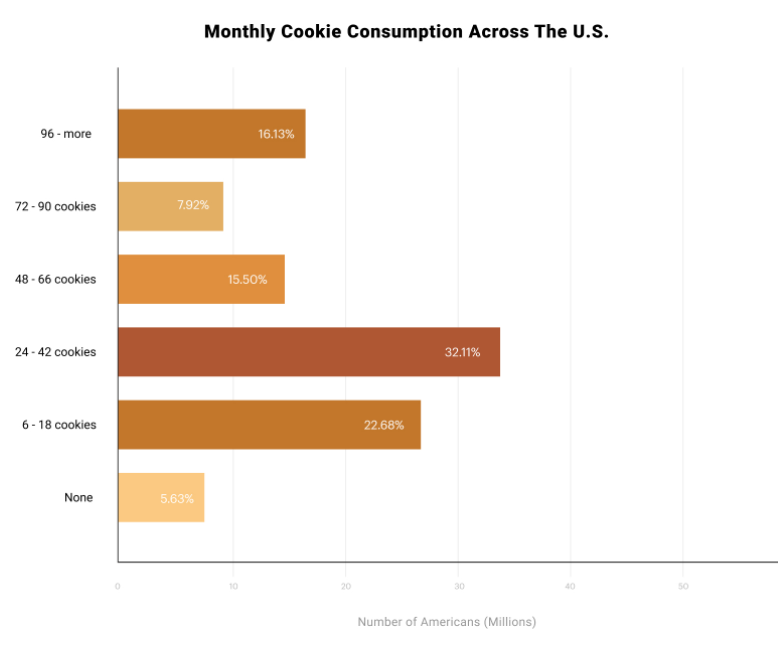
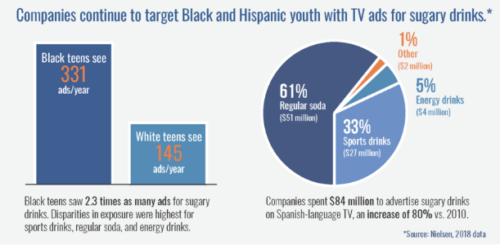
I could not keep up with the number of e-mails I got last week with the subject line “Have you seen this?”
“This” referred to an opinion piece in JAMA entitled Backlash Over Meat Dietary Recommendations Raises Questions About Corporate Ties to Nutrition Scientists.
Definitely up my alley.
The article describes the outraged reaction to a series of papers in the Annals of Internal Medicine last year arguing that recommendations to eat less meat are unfounded (I posted about this at the time). Some of the investigators involved in the meat papers turned out to have undisclosed ties to meat industry interests.
The JAMA article points out that the most outraged objections to the Annals papers came from investigators who have plenty of industry ties (plant-based) of their own.
My book, Unsavory Truth: How Food Companies Skew the Science of What We Eat, provides loads of evidence for a basic observation: research funded by food companies, regardless of the particular food studied, tends to produce results favorable to the sponsor’s interests.
It also describes how industry influence occurs at an unconscious level; recipients are unaware that they are being influenced.
How the influence gets expressed is also the subject of research. Bias most frequently turns up in the framing of the research question. It also turns up frequently in the interpretation of results.
Here is an example from a study of a healthy plant food—walnuts.
The study: Effect of a 2-year diet intervention with walnuts on cognitive decline. The Walnuts And Healthy Aging (WAHA) study: a randomized controlled trial. Aleix Sala-Vila, Cinta Valls-Pedret, Sujatha Rajaram, Nina Coll-Padrós, Montserrat Cofán, Mercè Serra-Mir, Ana M Pérez-Heras, Irene Roth, Tania M Freitas-Simoes, Mónica Doménech, Carlos Calvo, Anna López-Illamola, Edward Bitok, Natalie K Buxton, Lynnley Huey, Adam Arechiga, Keiji Oda, Grace J Lee, Dolores Corella, Lídia Vaqué-Alcázar, Roser Sala-Llonch, David Bartrés-Faz, Joan Sabaté, and Emilio Ros1. Am J Clin Nutr 2020;00:1–11.
Conclusions: Walnut supplementation for 2 y had no effect on cognition in healthy elders. However, brain fMRI and post hoc analyses by site suggest that walnuts might delay cognitive decline in subgroups at higher risk. These encouraging but inconclusive results warrant further investigation.
Conflicts of Interest: AS-V, SR, JS, and ER have received research funding through their institutions from the California Walnut Commission, Folsom, CA, USA. JS and ER were nonpaid members of the California Walnut Commission Scientific Advisory Council. ER was a paid member of the California Walnut Commission Health Research Advisory Group. JS has received honoraria from the California Walnut Commission for presentations. AS-V has received support from the CaliforniaWalnut Commission to attend professional meetings. All other authors report no conflicts of interest.
Comment: This looks to me like a classic example of interpretation bias. Although the study showed no effect of walnut supplementation, the authors interpret its overall results as encouraging. This is putting a positive spin on null results.
Walnuts—and other kinds of nuts—are plant foods with healthy fats. Why does the California Walnut Commission need to do this? So you will buy walnuts rather than hazelnuts, pecans, or macadamia nuts (all of which are sponsoring their own positive-result studies). Studies like these are mostly about marketing.
Questions of whether meat is healthy or unhealthy—and, if unhealthy, at what level of intake—are about much more than marketing. They need to be studied as objectively as possible. It’s best to keep industry influence far away from such studies.
Even if the science is done well from start to finish, researchers’ ties to food company sponsors give the appearance of conflicted interests. Such ties are best avoided from the get-go.
Follow-up