A reader writes:
Can you address the current food crisis outlining the many foods, long time frame, economic impact, and personal effort involved in this event?
I did not realize until I read the NPR email news brief this morning that one factory is the source of nine deaths, that multiple meat products are suspect, that many stores are involved, that sell-by dates extend into October, that products may be in appliances at home, and that all food in the appliance must be disposed of and that the empty appliance must be thoroughly cleaned.
My immediate response was to say that this is yet another recall due to foodborne illness and I’ve written previously about lots of these. But this one is especially tragic.
- The products—meat contaminated with Listeria—killed people who ate them.
- The plant in which they were produced is inspected daily by an on-site USDA inspector.
- Even so, the plant was especially dirty and unsafe.
The CDC reports: “Epidemiologic, laboratory, and traceback data show that meats sliced at delis, including Boar’s Head brand liverwurst, are contaminated with Listeria and are making people sick.”

This particular outbreak began in June.
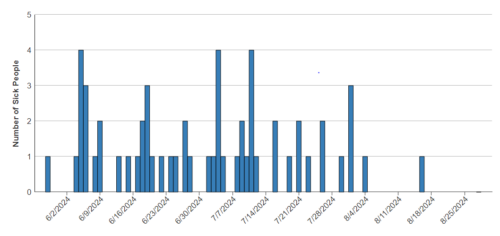
The USDA issued a recall notice at the end of July.
FSIS [USDA’s Food Safety and Inspection Service] is concerned that some product may be in consumers’ refrigerators and in retail deli cases. Consumers who have purchased these products are urged not to consume them and retailers are urged not to sell these products with the referenced sell by dates. These products should be thrown away or returned to the place of purchase. Consumers who have purchased these products are also urged to clean refrigerators thoroughly to prevent the risk of cross-contamination.
Boar’s Head published a list of the recalled products. These include several brands and product types.
CBS used FOIA to request USDA’s records of Boar’s Head inspection results. These take up 44 pages.
Food Safety News did a summary: “Inspection report reveals history of sanitation issues at Boar’s Head plant linked to deadly Listeria outbreak.”
Over a year of repeated sanitation failures — totaling 69 violations — at Boar’s Head’s Virginia plant, appears to have fueled the ongoing Listeria outbreak that has sickened 57 people across 18 states and claimed nine lives…The violations documented in the report include the presence of mold and mildew on surfaces that employees use to wash their hands, on the outside of steel vats and in holding coolers between smokehouses. These conditions are particularly concerning given the ability of Listeria monocytogenes to thrive in cold, moist environments.
CBS did a news video on the inspection results: “Mold, mildew and bugs linked to listeria outbreak, records show.”
Food safety lawyer Bill Marler is calling for a Congressional Investigation.
…years of inspection reports leave little doubt that the Boar’s Head plant’s HACCP [required safety plan] must have been either non-existent or used for toilet paper. It is hard to wrap your head around how food could be produced in these conditions by this company and under the un watchful gaze of FSIS inspectors.
Today’s New York Times points out that food safety recalls have additional consequences. The economic viability of the town that houses this Boar’s Head plant depends on it for employment and purchases of local services.
Comment
Few of the food safety issues I’ve written about recently involve meat. This is because of a major overhaul of USDA requirements for meat safety in the 1990s. Once the USDA required meat producers to develop and use HACCP [Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point] safety plans, outbreaks due to contaminated meat declined. When done right, these plans are highly effective. They require producers to identify places in production where contamination could occur, take steps to prevent contamination at those critical control points, and monitor to make sure those steps were taken. USDA inspectors are supposed to make sure all that happens.
But the inspection system has a built-in conflict of interest. The system is voluntary. The USDA cannot force compliance or order recalls. All it can do is to withdraw its inspectors, thereby forcing the plant to close. Nobody ever wants to do that.
The food safety system, divided between two agencies as it is (with different legislative mandates and different powers), needs an overhaul. Lives are at risk.
If you have any Boar’s Head products in your freezer, better take a look at what they are and get rid of any on the recall list.
And let your congressional representatives know that you want better food safety oversight.
Additions
Thanks to Michael Jacobson for sending a link to the Boar’s Head website and the company’s promotional video. After seeing it, this feels like even more of a tragedy.
Here’s Bill Marler’s legal complaint, just filed.
7-31-24: USDA withdraws inspectors
9-13-24: Boar’s Head announces plant closure