Industry-funded request for research proposals: The Beef Checkoff
I often get asked why I think industry funding biases research in ways that almost always ensure that results favor the sponsor’s interests.
A reader, Professor Michael Tlusty, sent me this excellent example (my emphasis in bold).
BEEF CHECKOFF 2026 HUMAN NUTRITION REQUEST FOR PROPOSALS NOW OPEN
On behalf of The Beef Checkoff, the National Cattlemen’s Beef Association (NCBA) is conducting a request for proposals (RFP) in Human Nutrition, to further understand beef’s nutritional qualities and define beef’s role in a healthy diet to nourish and optimize health at every life stage including research topics related to growth and development, healthy aging, and reduced risk of chronic disease.As part of their long-standing commitment to further scientific discovery, beef farmers and ranchers are invested in funding high quality, rigorous research — from observational epidemiological and clinical intervention trials to modeling and substitution analyses. As nutrition science continues to evolve, broadening and deepening the beef nutrition evidence base is essential to ensure that consumers have the most up-to-date information to make informed choices about the foods they eat.
The Human Nutrition Research Program follows a two-part application process, beginning with the submission of a pre-proposal. Pre-proposals are intended to be a brief overview of the proposed project….
Comment: If you want your project funded, you need to make sure it will demonstrate beef’s role in nourishing and optimizing health. If your project does not do this, it won’t get funded.
OK. Here’s your chance. Pre-proposals are due May 30 at 11:59 pm MT. Directions: Submit a Pre-Proposal

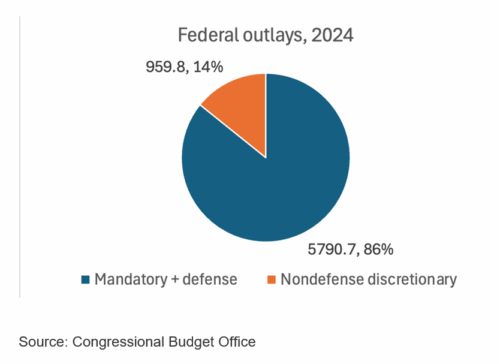
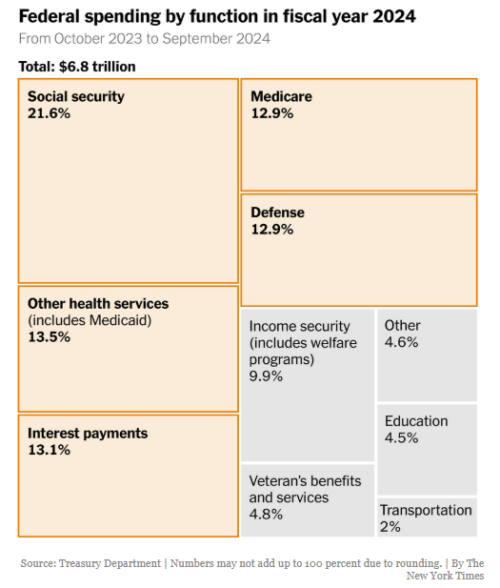
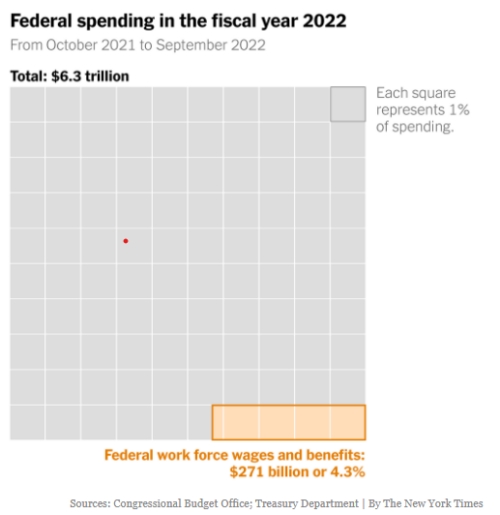 What this tells us is that if the entire government workforce were fired, it would only reduce federal expenditures by 4.3 percent.
What this tells us is that if the entire government workforce were fired, it would only reduce federal expenditures by 4.3 percent.

