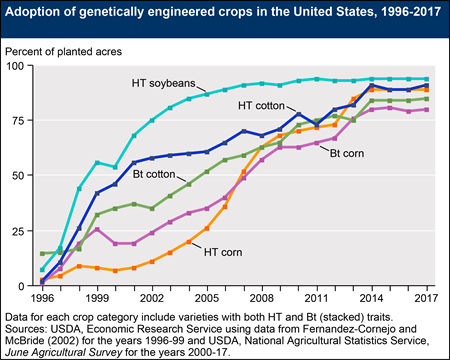
I’m having trouble keeping up with industry-sponsored nutrition research so will use this week’s posts to catch up. I’ll start with this one.
Nutrition journals often publish supplements on specific themes that are paid for by outside parties, food industry groups among them. The February 2016 issue of the Journal of Nutrition contains a supplement with the papers from the 2014 International Garlic Symposium: “Role of Garlic in Cardiovascular Disease Prevention, Metabolic Syndrome, and Immunology.”
To distinguish supplement papers from peer-reviewed journal articles, citations give page numbers with the letter S. The Journal of Nutrition’s exceptionally clear policy on supplement publications explains that organizers are expected to pay page charges of $75 per article and $300 per published page plus additional editorial costs as needed. It views supplements as paid advertisements and requires full disclosure of funding sources.
Here’s the disclosure for the garlic supplement.
The symposium was sponsored by the University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine and the University of Florida and co-sponsored by the American Botanical Council; the American Herbal Products Association; the ASN [American Society for Nutrition]; the Japanese Society for Food Factors; the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry; the Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science; and the Natural Products Association. The symposium was supported by Agencias Motta S.A.; Bionam; Eco-Nutraceuticos; Healthy U 2000 Ltd.; Magna; Mannavita Bvba; MaxiPharma; Medica Nord A.S.; Nature’s Farm Pte. Ltd.; Nature Valley W.L.L.; Organic Health Ltd.; Oy Valioravinto Ab; Purity Life Health Products L.P.; PT Nutriprima Jayasakti; Vitaco Health Ltd.; Vitae Natural Nutrition; Sanofi Consumer Health Care; Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; and Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd. The Chair of the conference and Scientific Program Coordinator for the supplement publication was Matthew J Budoff, Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA. Scientific Program Coordinator disclosures: MJ Budoff has been awarded research grants from Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd., and received an honorarium for serving as Chair of the conference. Vice-Chair and Supplement Coordinator for the supplement publication was Susan S Percival, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL. Supplement Coordinator disclosures: SS Percival has been awarded research grants from Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd., and received an honorarium for serving as Vice-Chair of the conference. Publication costs for this supplement were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This publication must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734 solely to indicate this fact. The opinions expressed in this publication are those of the authors and are not attributable to the sponsors or the publisher, Editor, or Editorial Board of The Journal of Nutrition [my emphasis].
Comment on scoring: Because they were presented at a symposium sponsored by food and supplement companies, all papers raise questions about industry sponsorship. That is why the Journal requires every paper in the supplement to repeat this funding disclosure in its entirety.
But for this particular symposium, some of the papers report additional funding by Wakunaga of America, a company that, no surprise, manufactures garlic supplements.
All of the papers produced results useful to the sponsor. Some of them, however, were independently funded and the authors report no links to the sponsor other than having given a talk at the meeting. They did not disclose who paid for travel and hotels and without any way to check, I must assume that they paid their own expenses to the meeting in San Diego. For the purposes of scoring, I’m not counting them as industry-funded, even though their presence at the symposium made it seem more scientifically credible.
Garlic Lowers Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Individuals, Regulates Serum Cholesterol, and Stimulates Immunity: An Updated Meta-analysis and Review. Karin Ried. J Nutr. 2016; 146:389S-396S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202192.
- Conclusions: Our review suggests that garlic supplements have the potential to lower blood pressure in hypertensive individuals, to regulate slightly elevated cholesterol concentrations, and to stimulate the immune system. Garlic supplements are highly tolerated and may be considered as a complementary treatment option for hypertension, slightly elevated cholesterol, and stimulation of immunity.
- Author disclosures: K Ried, no conflicts of interest. K Ried received travel sponsorship from Wakunaga of America Co. Ltd. to attend the 2014 International Garlic Symposium.
- Score: industry-positive
Chemical Assignment of Structural Isomers of Sulfur-Containing Metabolites in Garlic by Liquid Chromatography−Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance−Mass Spectrometry. Ryo Nakabayashi, Yuji Sawada, Morihiro Aoyagi, Yutaka Yamada, Masami Yokota Hirai, Tetsuya Sakurai, Takahiro Kamoi, Daryl D Rowan, and Kazuki Saito. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:397S-402S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202317.
- Conclusion: The ability to discriminate between such geometric isomers will be extremely useful for the chemical assignment of unknown metabolites in MS-based metabolomics.
- Supported, in part, by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan; Japan Advanced Plant Science Network; Japan Science Technology Agency (JST), Strategic International Collaborative Research Program (SICORP); and JST, Strategic International Research Cooperative Program (SICP).
- Score: industry-neutral
Garlic-Derived Organic Polysulfides and Myocardial Protection. Jessica M Bradley, Chelsea L Organ, and David J Lefer. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:403S-409S doi:10.3945/jn.114.208066.
- Conclusion: The beneficial health effects of garlic on cardiovascular health are dependent on multiple mechanisms. Furthermore, the mechanisms of action may be mediated by the active components in garlic.
- Supported by grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (1R01 HL092141, 1R01 HL093579, 1U24 HL 094373, and 1P20 HL113452; to DJL) and by the Louisiana State University Health Foundation in New Orleans.
- Score: Industry-neutral
Aged Garlic Extract Inhibits Human Platelet Aggregation by Altering Intracellular Signaling and Platelet Shape Change. Khalid Rahman, Gordon M Lowe, and Sarah Smith. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:410S-415S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202408
- Conclusion: These results indicate that AGE [Aged Garlic Extract] inhibits platelet aggregation by increasing cyclic nucleotides and inhibiting fibrinogen binding and platelet shape change.
- Funding: Supported by a grant from Wakunaga of America Co. Ltd. K Rahman and GM Lowe were in receipt of a grant from Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd. S Smith, no conflicts of interest.
- Score: industry-positive
Garlic and Heart Disease. Ravi Varshney and Matthew J Budoff. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:416S-421S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202333
- Conclusion: We conclude that garlic supplementation has the potential for cardiovascular protection based on risk factor reduction (hypertension and total cholesterol) and surrogate markers (CRP, PWV, and CAC) of atherosclerosis.
- Disclosures: The authors report no funding received for this study. R Varshney, no conflicts of interest. MJ Budoff receives funding from Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd.
- Score: industry-positive
The Role of Adiponectin in Cardiometabolic Diseases: Effects of Nutritional Interventions. Patricio Lopez-Jaramillo. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:422S-426S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202432
- Conclusions: Recently, it was reported that the administration of aged garlic extract and a single food intervention with pistachios can increase adiponectin concentrations in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Moreover, the Mediterranean diet is associated with higher adiponectin concentrations. Additional studies are needed to evaluate the potential benefits of increasing adiponectin by nutritional interventions in the treatment and prevention of cardiometabolic diseases.
- Funding: The author reports no funding received for this study.
- Score: Industry-neutral
Aged Garlic Extract Reduces Low Attenuation Plaque in Coronary Arteries of Patients with Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Randomized Double-Blind Study. Suguru Matsumoto, Rine Nakanishi, Dong Li, Anas Alani, Panteha Rezaeian, Sach Prabhu, Jeby Abraham, Michael A Fahmy, Christopher Dailing, Ferdinand Flores, Sajad Hamal, Alexander Broersen, Pieter H Kitslaar, and Matthew J Budoff. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:427S-432S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202424
- Conclusions: This study indicates that the %LAP [Low Attenuation Plaque] change was significantly greater in the AGE group than in the placebo group. Further studies are needed to evaluate whether AGE has the ability to stabilize vulnerable plaque and decrease adverse cardiovascular events.
- Disclosures: While the study was funded by Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd., the authors are solely responsible for the design, all study analyses, the drafting and editing of the paper and its final contents…S Matsumoto, R Nakanishi, D Li, A Alani, P Rezaeian, S Prabhu, J Abraham, MA Fahmy, C Dailing, F Flores, S Hamal, and A Broersen, no conflicts of interest. PH Kitslaar is employed by Medis Medical Imaging Systems and has a research appointment at the Leiden University Medical Center. MJ Budoff receives funding from Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd.
- Score: industry-positive
Aged Garlic Extract Modifies Human Immunity. Susan S Percival. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:433S-436S doi:10.3945/jn.115.210427
- Conclusions: These results suggest that AGE supplementation may enhance immune cell function and may be partly responsible for the reduced severity of colds and flu reported. The results also suggest that the immune system functions well with AGE supplementation, perhaps with less accompanying inflammation.
- Funding: Support for this research was provided by Wakunaga of America Co., Ltd. Author disclosures: SS Percival received travel expenses to the conference where this work was presented.
- Score: industry-positive
Bioavailability of Alfrutamide and Caffedymine and Their P-Selectin Suppression and Platelet-Leukocyte Aggregation Mechanisms in Mice. Jae B Park. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:437S-443S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202473
- Conclusions: These data show the adequate bioavailability of alfrutamide and caffedymine and their different mechanisms of suppressing PSE and PLA: alfrutamide exerts its effects only via COX inhibition, whereas caffedymine works through both COX inhibition and cAMP amplification.
- Funding: Supported by the USDA (project 8040-51000-057-00).
- Score: Industry-neutral
Garlic Influences Gene Expression In Vivo and In Vitro. Craig S Charron, Harry D Dawson, and Janet A Novotny. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:444S-449S doi:10.3945/jn.114.202481
- Conclusion: Measuring mRNA gene expression in whole blood may provide a unique window to understanding how garlic intake affects human health.
- Support: CSC, HDD, and JAN were supported by the USDA.
- Score: Industry-neutral.
Development of an Analytic Method for Sulfur Compounds in Aged Garlic Extract with the Use of a Postcolumn High Performance Liquid Chromatography Method with Sulfur-Specific Detection. Toshiaki Matsutomo and Yukihiro Kodera. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:450S-455S doi:10.3945/jn.114.208520
- Conclusion: We developed a rapid postcolumn HPLC method for both qualitative and quantitative analyses of sulfur compounds, and this method helped elucidate a potential mechanism of cis-S1PC and SAMC action in AGE.
- Acknowledgment: The authors thank Takami Oka of Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. for his kind guidance for this study and critical review of the manuscript.
- Score: Industry-positive
Pharmacokinetics of S-Allyl-L-cysteine in Rats Is Characterized by High Oral Absorption and Extensive Renal Reabsorption. Hirotaka Amano, Daichi Kazamori, and Kenji Itoh. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:456S-459S doi:10.3945/jn.114.201749
- Conclusion: The pharmacokinetics of SAC in rats were characterized by high oral absorption, limited metabolism, and extensive renal reabsorption, all of which potentially contribute to its high and relatively long-lasting plasma concentrations.
- Acknowledgment: We thank Takami Oka of Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co. for his valuable advice, critical reading of the manuscript, and helpful suggestions.
- Score: Industry-positive
Aged Garlic Extract Suppresses the Development of Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E–Knockout Mice. Naoaki Morihara, Atsuko Hino, Takako Yamaguchi, and Jun-ichiro Suzuki. J. Nutr. 2016; 146:460S-463S doi:10.3945/jn.114.206953
- Conclusion: These data suggest that the antiatherosclerotic activity of AGE is at least partly due to the suppression of inflammation and lipid deposition in the vessels during the early stage of atherosclerotic development in ApoE-KO mice.
- Acknowledgment: We thank Takami Oka of Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., for his helpful advice, encouragement, and critical reading of this manuscript; Yukihiro Kodera of Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., for the preparation of AGE; and Tadamitsu Tsuneyoshi of Wakunaga Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., for his technical advice.
- Score: Industry-positive
This makes 8 industry-positives from this journal supplement.
But let me add one more on this topic, sent by a reader:
The effect of aged garlic extract on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors in uncontrolled hypertensives: the AGE at Heart trial. Karin Ried Nikolaj Travica, Avni Sali. Integrated Blood Pressure Control, 27 January 2016.
- Conclusion: Our trial suggests that aged garlic extract is effective in reducing peripheral and central blood pressure in a large proportion of patients with uncontrolled hypertension, and has the potential to improve arterial stiffness, inflammation, and other cardiovascular markers in patients with elevated levels. Aged garlic extract was highly tolerable with a high safety profile as a stand-alone or adjunctive antihypertensive treatment.
- Funding: This trial was supported by a grant from Wakunaga of America Co Ltd, who supplied trial capsules and provided funding for costs of tests and research assistance. Wakunaga of America was not involved in study design, data collection, analysis, or preparation of the manuscript…The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
- Score: industry-positive, of course.
This brings the score since last March to 119 industry-positives/11 industry-negatives.

 How’s that for reassuring?
How’s that for reassuring?