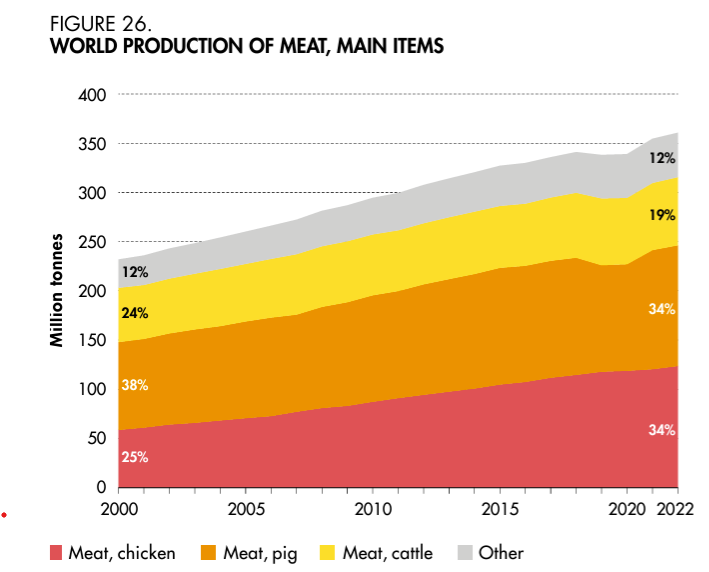
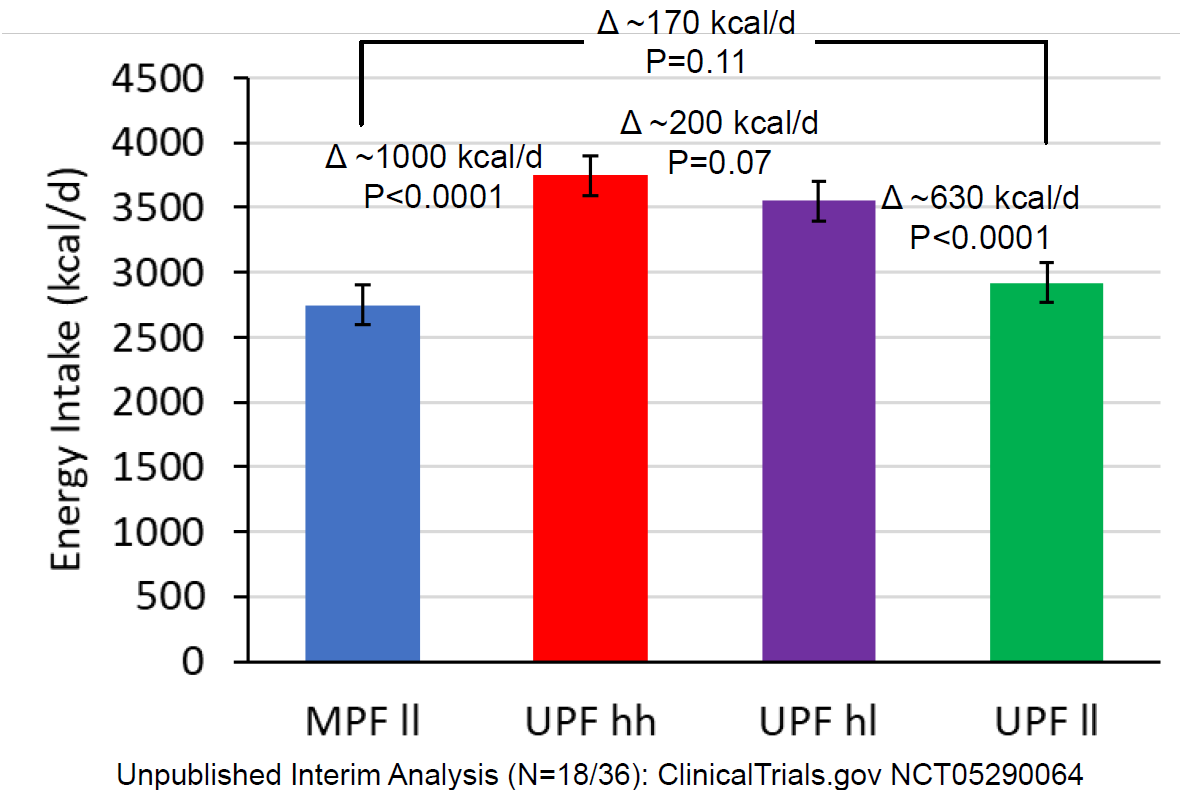
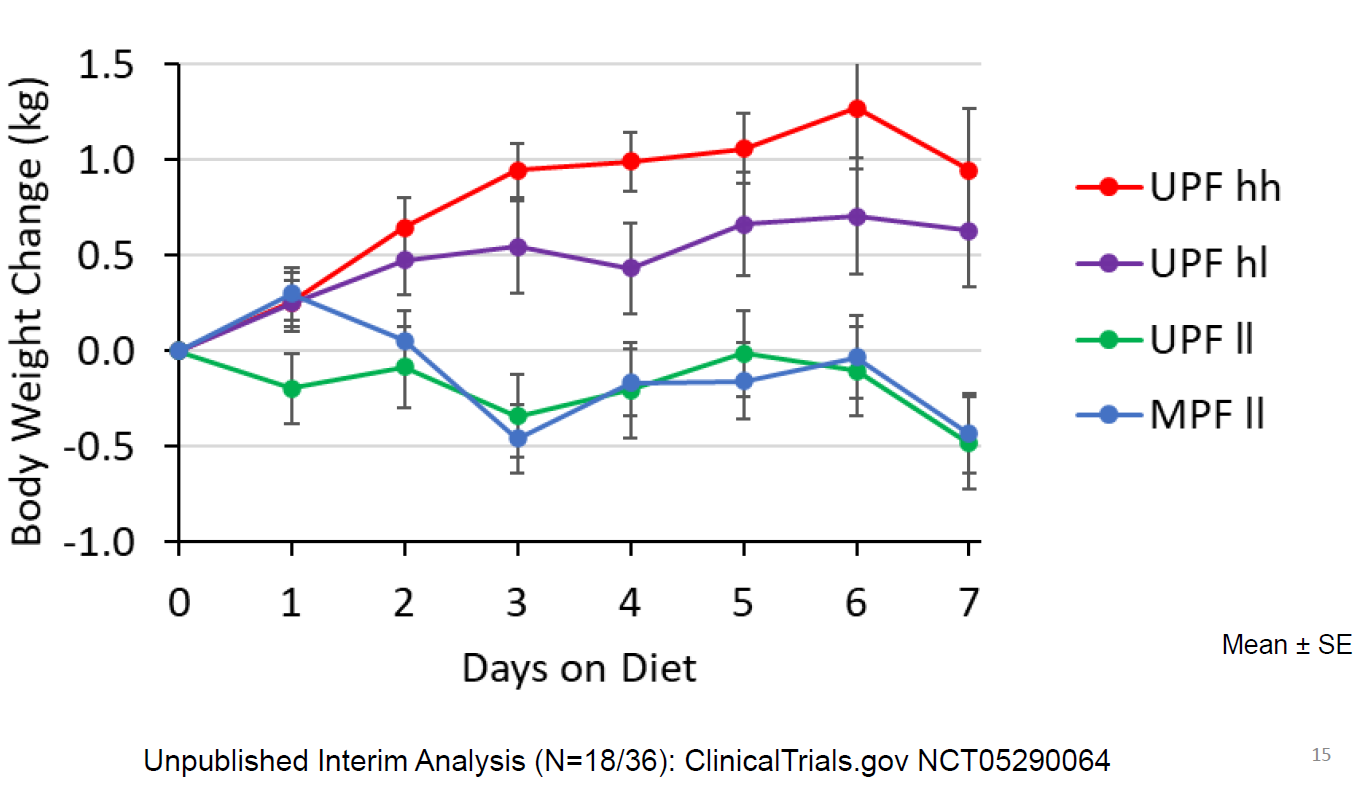
Santa Cruz passes soda tax!
The Santa Cruz Sentinal says Measure Z soda tax officially passes in Santa Cruz.
According to the Santa Cruz County Elections Department, 15,780 votes were counted in favor of the ballot initiative, or about 52%, and 14,364 votes, or approximately 48%, were counted against the passage of Measure Z….“Despite being outspent $1.9 million to our $85,000 by corporate special interests, the people of Santa Cruz stood strong and made their voices heard.”
The tax has been a long time coming. It was first proposed in 2018, but was blocked by a California state act backed by the soda industry which prevented taxes on groceries until 2031. Lawsuits overturned the penalty provision of the act, which allowed tax proposals to continue.
Politico reviews the history of soda tax fights in California.
Berkeley voted to renew its existing tax, no doubt for these reasons and despite being outspent tenfold.
Research looking at the last decade of Berkeley’s sugary drink tax shows the tax is working: Consumption of sugary drinks dropped by 52% and water increased by 29% among Berkeley residents in diverse neighborhoods with a large proportion of Black and Latino residents. In addition, 16 hydration stations have been installed and $5.7 million has been invested into 18 community gardens at Berkeley Unified School District sites. Funding has also supported vital public health and sustainability programs through organizations like Lifelong Medical Care, Healthy Black Families, The Multicultural Institute, YMCA of the East Bay Early Childhood Impact and The Ecology Center.
The point of all this:
Sugary drinks are the largest source of added sugar in the American diet. The American Heart Association recommends no more than six teaspoons of added sugar per day for women and nine teaspoons for men. One 12-ounce can of sugared soda contains about 10 teaspoons.