Sugars consumption dropping for 20 years straight
The USDA’s Economic Research Service, back on the job, has the latest statistics on the availability of sugars in the U.S. food supply.
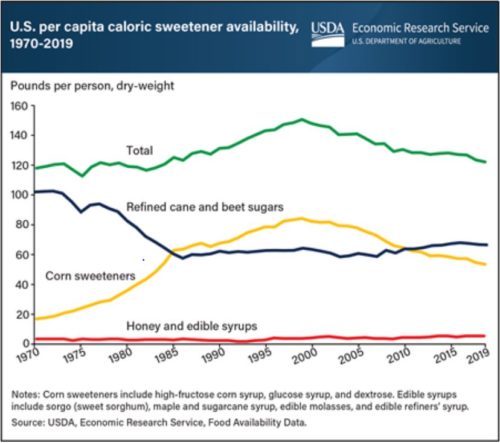
Availability means the amount produced plus imports less exports, per year, per capita.
It is not the same as consumption (availability is likely to be higher), but it is an accurate indicator of trends.
The chart shows:
- Availability of sugars peaked in about 1999 and has been going down ever since.
- The increase was almost entirely in corn sweeteners—high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) and the like.
- The rise in HFCS was due to its substitution for sucrose (the sugar in beets and cane), in soft drinks starting in the late 1970s. Soft drinks account for close to half of available sugars.
- Cane and beet sugar (sucrose) fell with substitution of HFCS, but started to increase again as HFCS got a bad reputation.
- Total availability of all sugars is now around 120 pounds per person per year.
What does 120 pounds per capita per year mean?
- Calculation: 120 pounds per capita x 454 grams per pound divided by 365 days per year = 149 grams per day per capita (approaching 40 teaspoons)
- This means about 600 calories available from sugars per day per person (which, in turn, refers to every man, woman, child, and infant in the country). This is a lot of sugars.
Current Dietary Guidelines say sugars should not exceed 10% of daily calories. For diets of 2000 calories a day, that means no more than 50 grams of sugars (one gram of sugar = about 4 calories).
Therefore, the U.S. food supply provides at least three times the upper amount of sugars recommended.
Pretty much everyone would be healthier eating less sugar, if for no other reason than that they provide calories but minimal or no nutrients.
Their lack of nutritional value applies to sugars of all kinds, refined and unrefined, no matter their source: beets, cane, honey, sorghum, or maple trees.
The downward trend is in the right direction.



 Peter Hoffman, the chef-owned of the much loved and late-lamented Savoy restaurant in Manhattan’s SoHo has written an account of its rise and fall along with a close examination of what went into it, foods, ingredients, and emotions.
Peter Hoffman, the chef-owned of the much loved and late-lamented Savoy restaurant in Manhattan’s SoHo has written an account of its rise and fall along with a close examination of what went into it, foods, ingredients, and emotions.