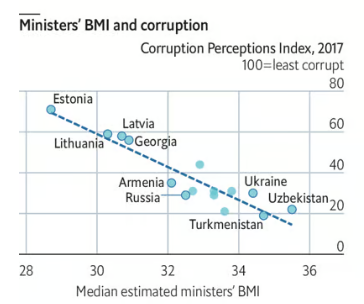
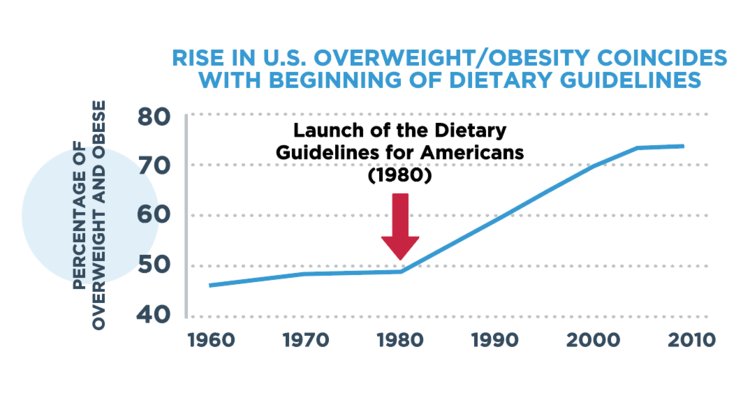
The latest on the forthcoming (eventually) farm bill
Every five years or so, we have to deal with another farm bill. Like the dietary guidelines, also every five years, the farm bill doesn’t really change much. The arguments about both don’t change either. So here we go again.
And just so you know where i”m coming from on this, here are my classic thoughts on the matter: “The farm bill drove me insane.”
A quick summary of why it does: it’s a collection of dozens if not hundreds, of programs, each with its own constituency and lobbyists, and too complicated for outsiders (like me) to understand. The elephant in the farm bill is SNAP, which takes up 80% or so of the funding and accounts for most of the fights. What SNAP is doing there is a long story, but don’t even think about removing it; take it out and neither food assistance nor farm supports would have enough votes to pass.
On May 1, Debbie Stabenow (D-MI), chair of the Senate Agriculture Committee introduced her version of this year’s delayed farm bill: The Rural Prosperity and Food Security Act.
A full summary of the bill is here. (Note: it’s vague on details)
A section-by-section is here. (Note: it’s 94 pages)
Title summaries
- Certainty for All Farmers
- Conservation
- Trade Promotion and International Food Aid
- Nutrition
- Credit
- Rural Development
- Research
- Forestry
- Energy
- Horticulture
- Miscellaneous
The House Committee’s counter-proposal is available here.
It’s too early for me to get into the weeds on this.
On SNAP (the Nutrition title), some advocates will be pushing for making it healthier as well as increasing benefits.
On farm supports (Certainty for All Farmers title, and others), advocates for animal rights, young farmers, and Black farmers will want more than they have received in the past. Most of what’s in the farm bill goes to support feed for animals and fuel for automobiles.
On “specialty crops,” (translation: food for people) in the Horticulture title, I was amused to see a $100 million increase per year, which sounds like a lot but is barely a rounding error in a bill costing $100 billion or more a year.
The farm bill ought to be an opportunity to bring agricultural policy in line with health policy and to focus on producing food healthy for people and the planet.
Well, the details are still to come, and reconciliation of the two versions is still a long way off . Stay tuned.