One reason why we need a more rational food policy: farm payments
I am all for making sure that farmers make a decent living but most agricultural subsidies go to Big Ag—the producers of corn and soybeans fed mainly to animals or, in the case of corn, as ethanol for car fuel.
These taxpayer-funded payments are enormous and represent increasing percentages of the income of Big Ag.
For example, see this chart from the Wall Street Journal.
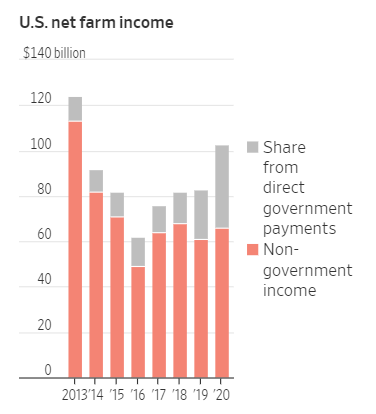
As part of the Trump administration’s effort to get votes from farmers and ranchers, it pledged $37.2 billion to them in the spring and summer with an addition $14 billion in September.
Why is this about the election? The Washington Post says “Trump’s farmer bailout gave $21 billion to red counties and $2.1 billion to blue ones.”
At a campaign rally in Wisconsin last week, President Trump didn’t mince words about how much his administration had done to bolster the economic fortunes of farmers…I gave $28 billion to the farmers, many of them right here, $28 billion, $12 billion and $16 billion, two years”… That redistribution was facilitated through the Agriculture Department’s Market Facilitation Program. According to data obtained by the Environmental Working Group through a Freedom of Information Act request, that program disbursed more than $23 billion in the 2018 and 2019 program years.
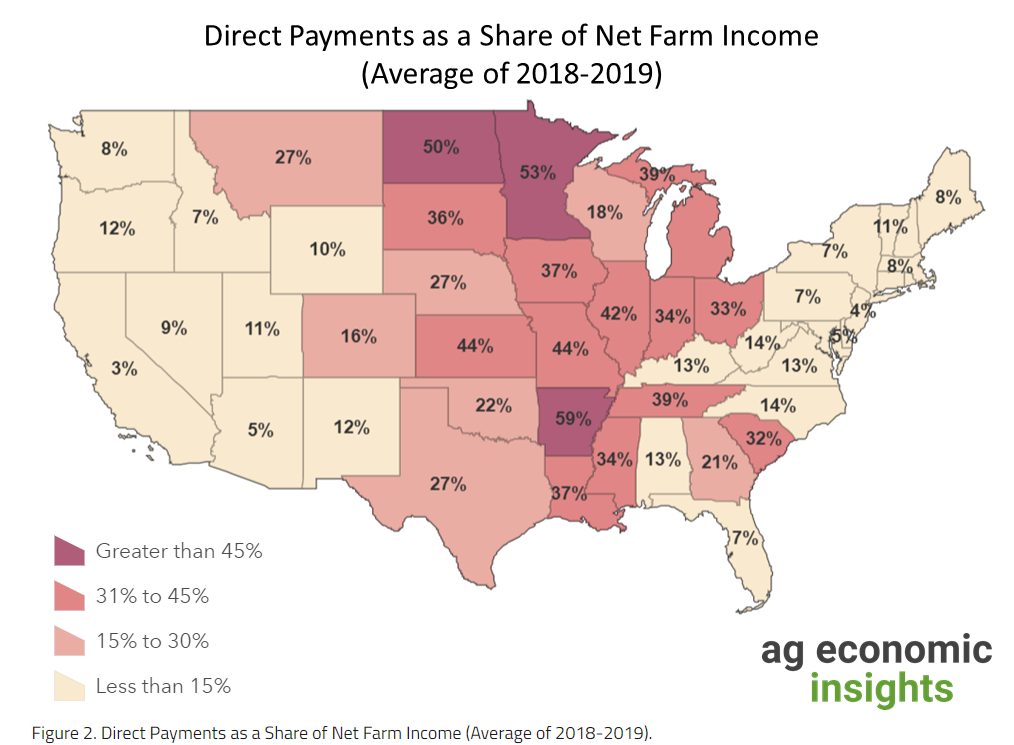
From a report from Agricultural Economic Insights: USDA’s direct payments to Big Ag will equal 36% of net farm income, up from 22% in 2018=2019. These payments used to account for around 10% of net farm income.
Check out its map:
Finally, it’s good to review the big picture of what happened to food and farming under Trump. Civil Eats has an excellent review by Lisa Held.
To offset the effects of the tariffs, in 2018, USDA began distributing cash payments through the Commodity Credit Corporation at unprecedented levels, with no appropriations or oversight from Congress. In 2020, as the pandemic hit the farm economy, it added another source of government payments via the Coronavirus Food Assistance Program (CFAP). Overall, Trump’s USDA has handed out more government dollars to farmers than any administration prior. In both 2019 and 2020, more than 40 percent of farm incomes came from federal assistance—the only thing keeping farm incomes afloat.
Those payments have been controversial because they have almost exclusively benefited the largest farms and agriculture companies. Two-thirds of the trade aid payments went to agriculture producers in the top 10 percent, including corporations, such as the $67 million paid to JBS USA, a subsidiary of the Brazilian-owned meatpacking giant. Small farms, especially diversified operations and those run by socially disadvantaged Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC) farmers, have largely been unable to access CFAP assistance.
All of this leaves plenty of room for improvement.
President-elect Biden: get to work!



