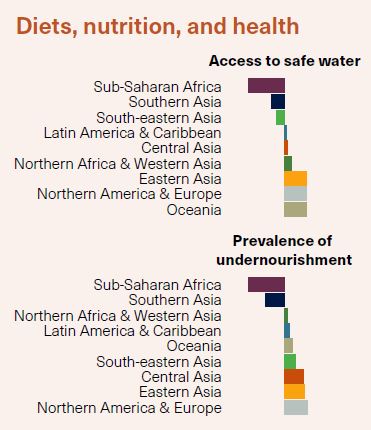
Weekend reading: Ethical Eating
Jennifer Cognard-Black and Melissa A Goldthwaite, eds. Good Eats: 32 Writers on Eating Ethically. New York University Press, 2024.

I did a blurb for the back cover:
In Ethical Eating, authors from all walks of life relate their daily struggles—moral as well as economic—to eat diets that promote human and environmental health and meet deeply held principles of food equity and social justice. Their accounts of these struggles are sometimes funny, always moving, and entirely recognizable by anyone trying to eat ethically.
This book contains several dozen short-to-medium length essays describing authors’ struggles—I use the word advisedly—to figure out how to eat in today’s impossibly complicated food system.
The book is designed to be used in food literature courses, and I can see why.
Each essay raises subject-to-debate issues about the costs and consequences of making principled dietary choices on a day-to-day basis while living with the usual complexities of life.
The writers are almost all unknown to me, so the book is an introduction to the concerns of people who care about the same issues I do, although often in very different ways.
Amazon has examples from the text and the Table of Contents . Here’s a sample of the TOC—there’s much more in the book: