Here’s how I learned about this one: Unilever, Nestlé and Coca-Cola villainised for government scientist ties. Mondelēz International, Tate & Lyle, Pepsico and a host of other global food and drink manufacturing majors face fresh scrutiny over their links to government-advising scientists…. Read more
Villainized? Isn’t this just business as usual?
Not exactly. An analysis in the BMJ (formerly British Medical Journal) says UK government’s nutrition advisers are paid by world’s largest food companies(see BMJ 2024;386:q1909).
The authors examined declared links between members of SACN (The UK Government’s Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition) and the food and drinks industry.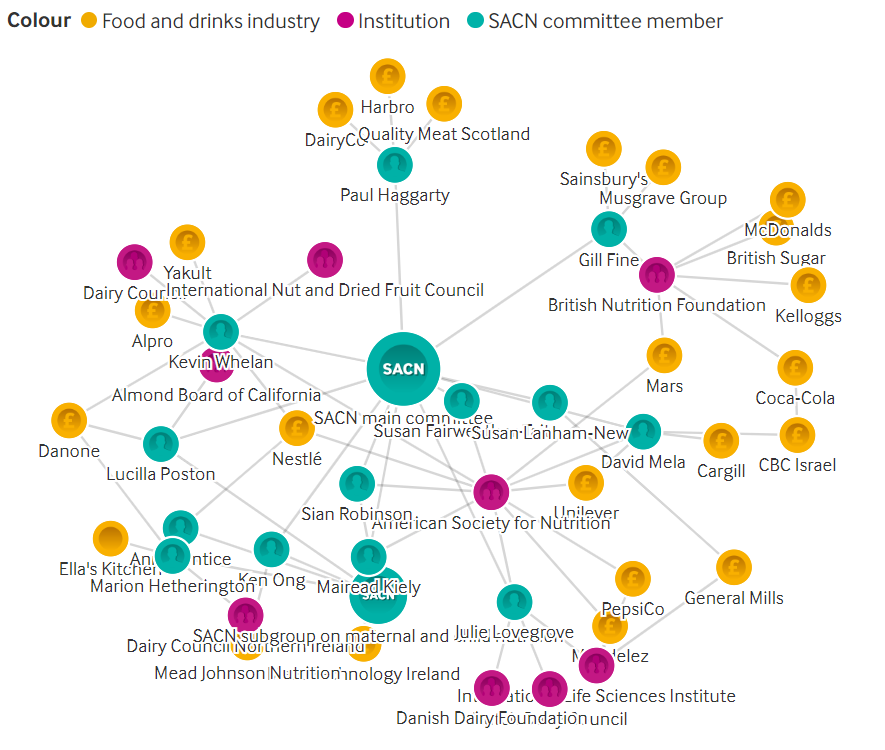
:
The study found
More than half of the experts on the UK government’s advisory panel on nutrition have links to the food industry…Campaigners say that these conflicts of interests at the heart of policy making are detrimental to public health. Others say that they reflect the lack of funding for nutrition research and that removing experts with industry links from SACN would “diminish” its expertise..
Six members of SACN are members of the American Society for Nutrition, which is funded by Mars, Mondelez, Nestlé, PepsiCo, and the Sugar Association, among others…SACN’s current work includes reviewing the evidence over ultraprocessed foods, artificial sweeteners, and plant based food and drink…Experts including van Tulleken and Percival say that SACN did not do enough to present the case for tougher regulation on ultraprocessed foods.
The usual excuses are
- Independent experts are unavailable
- Other research funding is not available
- The funding has no influence
Much research, reviewed in my book Unsavory Truth: How the Food Industry Skews the Science of What We Eat, demonstrates these claims to be false. Despite that research, recipients of industry largesse do not recognize the influence and typically deny it.
The more analyses like this one, the better.
Caveat
For a discussion of why disclosure is not sufficient (it causes “willy-waving”), see this in the BMJ.


