Join Health Affairs for a virtual conversation between me and Angela Odoms-Young of Cornell University discussing the evolution of US food and nutrition policy, the current policy landscape, and thoughts on what lies ahead. It’s at 1:00 p.m. EDT. To join the Webinar, click here.
What Covid-19 is doing to meatpacking workers and communities
A scientific report in Proceedings of the National Academies titled Livestock plants and COVID-19 transmission,” demonstrates the impact of Covid-19 on workers in meat and poultry processing plants.
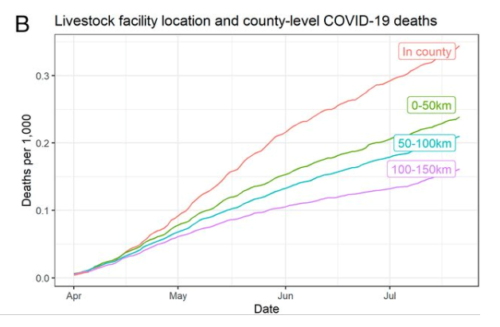
Our study suggests that, among essential industries, livestock processing poses a particular public health risk extending far beyond meatpacking companies and their employees. We estimate livestock plants to be associated with 236,000 to 310,000 COVID-19 cases (6 to 8% of total) and 4,300 to 5,200 deaths (3 to 4% of total) as of July 21….This study shows that meat and poultry slaughter plants were in fact vectors of the disease…Researchers found that poultry plants showed a significant relationship with COVID-19 cases, with pork plants showing the strongest relationship. Beef plants showed the strongest relationship with deaths from the illness.
The USDA has done its own analysis: “The share of all COVID-19 cases in nonmetro [rural] areas has been growing since late March, increasing from 3.6 percent on April 1 to 15.6 percent on December 7.”
Among nonmetro counties, the highest COVID-19 case rates are found in farming-dependent and manufacturing-dependent counties. The high prevalence of COVID-19 in manufacturing-dependent counties is due partly to higher COVID-19 case rates in meatpacking-dependent counties (those in which 20 percent or more of employment is in the meatpacking industry), almost all of which are manufacturing-dependent counties.
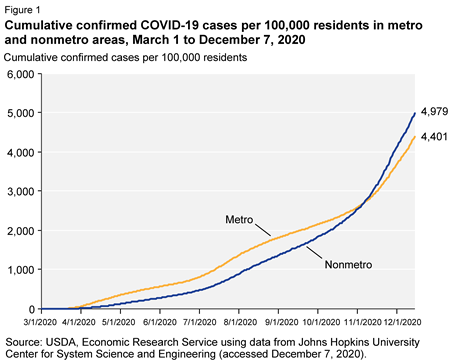
But another USDA report, specifically about the meatpacking industry, looks to me as though it is hiding what is happening in those plants. It includes a chart indicating no special increase in cases among meatpacking workers. No surprise, if meatpacking plants are epicenters that spread the infection to the local community (but the report doesn’t say that).
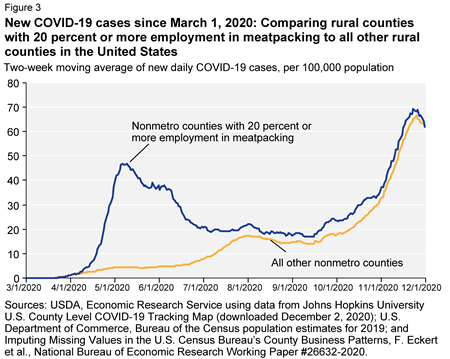
What it does say is this:
The two-week moving average number of new daily cases rose in meatpacking-dependent counties through the remainder of April, reaching a peak of nearly 50 cases per 100,000 by the end of the month. This two-week moving average was more than 10 times the prevalence seen in other rural counties. Even though cases in meatpacking-dependent counties started to decline in the month of May, they remained significantly higher compared to other rural counties, falling to just under seven times the number of average daily cases by the end of May.…Even though meatpacking-dependent counties are dealing with a second wave, the surge in rural new cases does not appear to be driven by new outbreaks in the meatpacking industry. Meatpacking-dependent counties have maintained an almost identical pattern to other rural counties for a fifth straight month.
Confused? Me too. This looks like a whitewash.
Is this one result of the USDA’s moving the Economic Research Service out of Washington DC to Kansas City, a move clearly meant to—successfully—decimate the agency?
Politico asks: can the ERS move be reversed? Not easily, alas.
It’s a good thing independent scientists and investigators are keeping an eye on this situation.
Leah Douglas of the Food and Environment Reporting Network (FERN) deserves much praise for tracking infections and deaths among farm and meatpacking workers.

