The theme: Feeding the Shared Future: A Call to Action.
Information and registration for the summit is here.
I’m speaking in the last afternoon session in conversation with Dan Giusti.
It’s at the DREAM Charter School,20 Bruckner Boulevard Website
My colleague, Lisa Young, forwarded this ad to me from the weekend’s Wall Street Journal.

In case it’s too small for you to read, the ad makes some eyebrow-raising points:
This, in case it is not instantaneously obvious, is part of the beef industry’s well documented effort to fight concerns about the well documented role of beef production in climate change.
The ad is paid for by the Beef Checkoff, one of the USDA-sponsored marketing and promotion programs funded by what is essentially a tax—the “checkoff”—on producers. I recently wrote about how the Beef Checkoff funds research in this industry’s interest.
The ad cites research studies supporting its statements, but these are cherry-picked.
Estimates of the percent of greenhouse gases contributed by lifestock production vary, but the most widely accepted range from 14% to 18%. Beef accounts for at least 10%.
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN, for example, says:
Total emissions from global livestock: 7.1 Gigatonnes of Co2-equiv per year, representing 14.5 percent of all anthropogenic GHG emissions…Cattle (raised for both beef and milk, as well as for inedible outputs like manure and draft power) are the animal species responsible for the most emissions, representing about 65% of the livestock sector’s emissions…feed production and processing (this includes land use change) and enteric fermentation from ruminants are the two main sources of emissions, representing 45 and 39 percent of total emissions, respectively.
The New York Times describes foods that have the largest impact on climate change.
Meat and dairy, particularly from cows, have an outsize impact, with livestock accounting for around 14.5 percent of the world’s greenhouse gases each year. That’s roughly the same amount as the emissions from all the cars, trucks, airplanes and ships combined in the world today.
In general, beef and lamb have the biggest climate footprint per gram of protein, while plant-based foods tend to have the smallest impact. Pork and chicken are somewhere in the middle.
A study published in Science calculated the average greenhouse gas emissions associated with different foods. The New York Times summarizes its results:
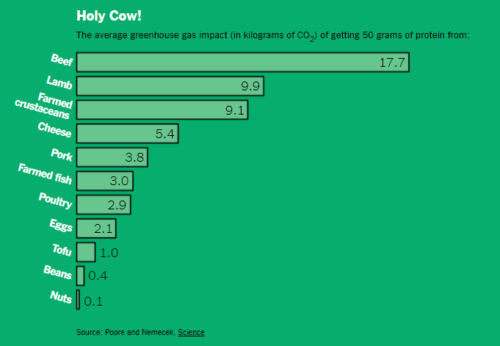
Beef production creates emissions of methane as well as carbon dioxide from multiple sources: feed production, cow burps, manure production, etc.
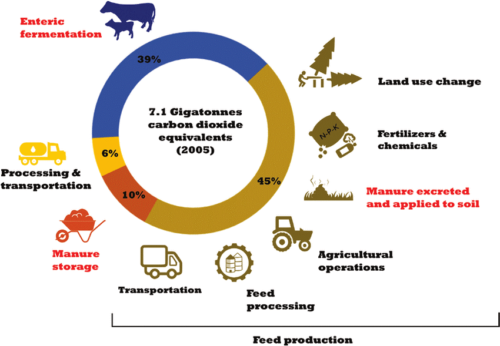
Beef production that involves grazing on grasslands could meet sustainability goals, but beef cattle raised in feedlots cannot.
There are plenty of environmental reasons for eating less beef, and these are on top of health reasons.
The Beef Checkoff ad does not tell the whole story, alas.
Addition
Lisa reminds me that the cost of a full-page color ad in the Wall Street Journal runs around $200,000.