This session is on Practicing Food Studies. It will be at 5;00 p.m. Details to come.
Fish politics: The FDA’s updated policy on eating fish while pregnant
Eating fish presents difficult dilemmas (I evaluate them in five chapters of What to Eat).
This one is about asking pregnant women to weigh the benefits of fish-eating against the hazards of their toxic chemical contaminants to the developing fetus.
The Dietary Guidelines tell pregnant women to eat 2-to-3 servings of low-mercury fish per week (actually, it’s methylmercury that is of concern, but the FDA calls it mercury and I will too).
But to do that, pregnant women have to:
- Know which fish are low in mercury
- Recognize these fish at the supermarket, even if they are mislabeled (which they sometimes are).
Only a few fish, all large predators, are high in mercury. The FDA advisory says these are:
- Shark
- Swordfish
- King Mackerel
- Tilefish
What? This list leaves off the fifth large predator: Albacore (white) tuna. This tuna has about half the mercury as the other four, but still much more than other kinds of fish.
The figure below comes from the Institute of Medicine’s fish report. It shows that fish highest in omega-3 fatty acids, the ones that are supposed to promote neurological development in the fetus and cognitive development in infants, are also highest in mercury.
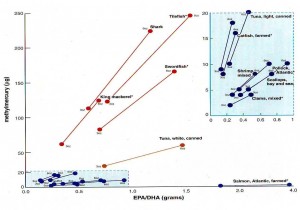
White tuna is the line toward the bottom. The ones in the blue boxes are all much lower in omega-3s and in mercury except for farmed Atlantic salmon (high in omega-3s, very low in mercury).
What’s going on here?
- Tuna producers know you can’t tell the difference between white and other kinds of tuna and don’t want you to stop eating tuna during pregnancy.
- The data on the importance of eating fish to children’s cognitive development are questionable (in my opinion). The studies are short term and it’s difficult to know whether the small gains in early cognitive development that have been reported make any difference a few months later.
- The FDA must be under intense pressure to promote fish consumption.
I think it is absurd to require pregnant women to know which fish to avoid. In supermarkets, fish can look pretty much alike and you cannot count on fish sellers to know the differences.
Other dilemmas:
- Even smaller fish have PCBs, another toxin best avoided by pregnant women, if not everyone.
- The world’s seafood supply is falling rapidly as a result of overfishing.
- Half of the mercury in seafood derives from emissions from coal-burning power plants. The best way to reduce mercury in fish is to clean up the emissions from those plants, but plant owners want to avoid the expense.
That’s fish politics, for you.
The FDA documents:
- Press Release: FDA and EPA Issue Draft Updated Advice for Fish Consumption
- FDA and EPA Draft Updated Advice for Fish Consumption (open for public comment)
- Federal Register Notice – Environmental Protection Agency and Food and Drug Administration Advice About Eating Fish: Availability of Draft Update
- Consumer Update: New Advice: Some Women and Children Should Eat More Fish
- Dietary Guidelines for American’s 2010
- Quantitative Assessment of the Net Effects on Fetal Neurodevelopment from Eating Commercial Fish

